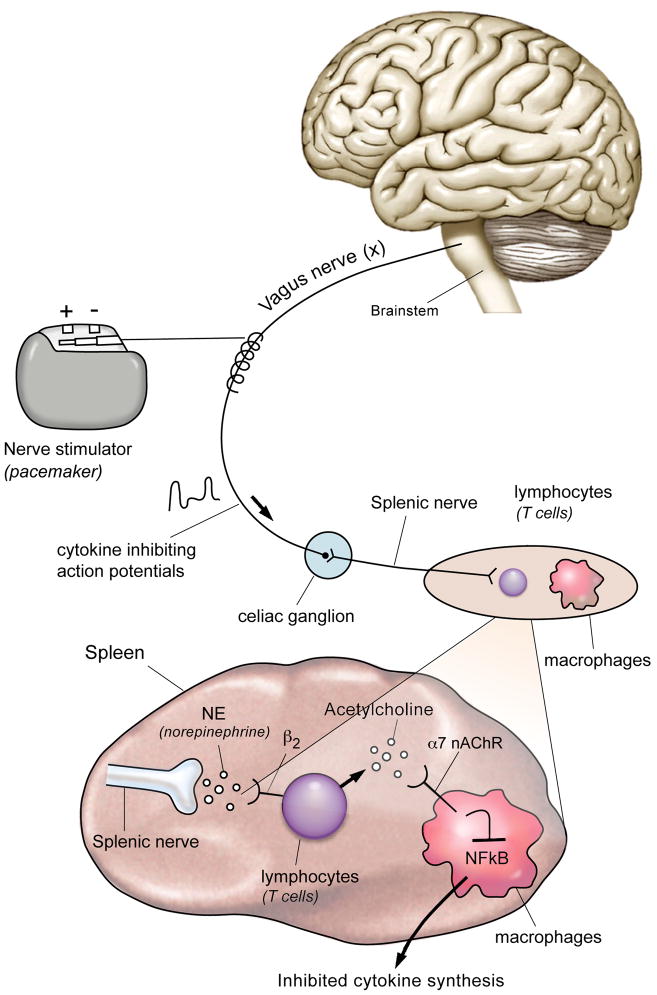
Figure 1.
Action potentials transiting the vagus nerve synapse in the celiac ganglion, the origin of the splenic nerve. The splenic nerve controls lymphocytes in the spleen, which can produce acetylcholine that interacts with α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors expressed on cytokine producing macrophages. Intracellular signal transduction through this receptor inhibits the activity of NFκB to suppress cytokine production. Nerve stimulators can provide an identical signal to initiate the antiinflammatory pathway, an approach that reverse signs and symptoms in preclinical disease models of arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, ischemia-reperfusion injury, heart failure, pancreatitis, sepsis, and other syndromes.