Figure 1. Damage sensitivity of rad50hook mutants.
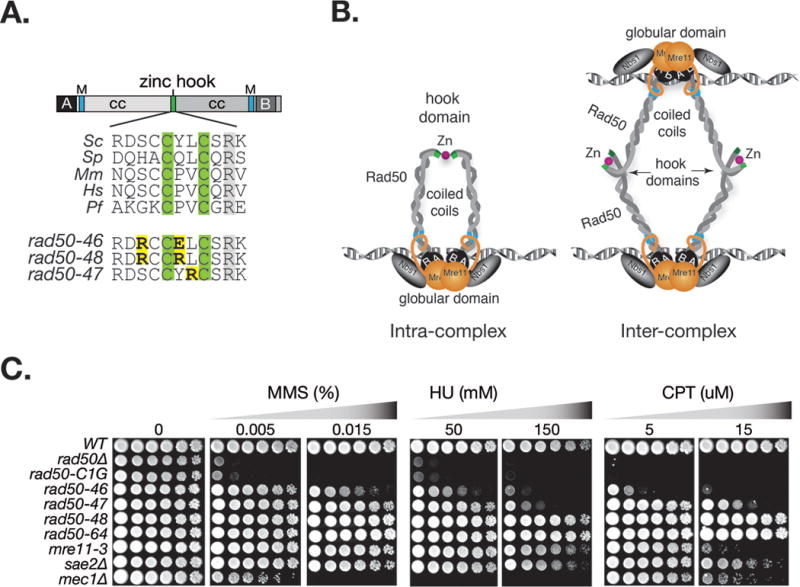
A. Rad50 primary domain structure and multiple sequence alignment of the central portion of the Rad50 hook domain. The zinc coordinating hook cysteines are highlighted in green and in yellow the S. cerevisiae rad50hook alleles, rad50-46 (S685R Y688E), rad50-4 7 (L689R) and rad50-48 (S685R Y688R). Annotations: coiled coil (cc), Walker A (A), Walker B (B), Mre11 interaction interface (M); Sc, S. cerevisiae; Sp, S. pombe; Mm, M. musculus, Hs, H. sapiens; Pf, P. furiosus. B. Schematic illustration of Rad50 hook dimerization between Rad50 proteins within a dimeric Mre11 complex assembly (intra-complex) or between Rad50 molecules in separate Mre11 complex dimeric assemblies (inter-complex). C. Sensitivities of rad50hook mutants to the indicated concentration of MMS, HU and CPT. The rad50-46 mutational residues were flipped in rad50-64 (S688E Y688R). Plates were incubated at 30°C. Outcomes at other incubation temperatures are given in Figure S1.
