Figure 4. rad50hook mutants are defective in telomere maintenance and Tel1 checkpoint signaling.
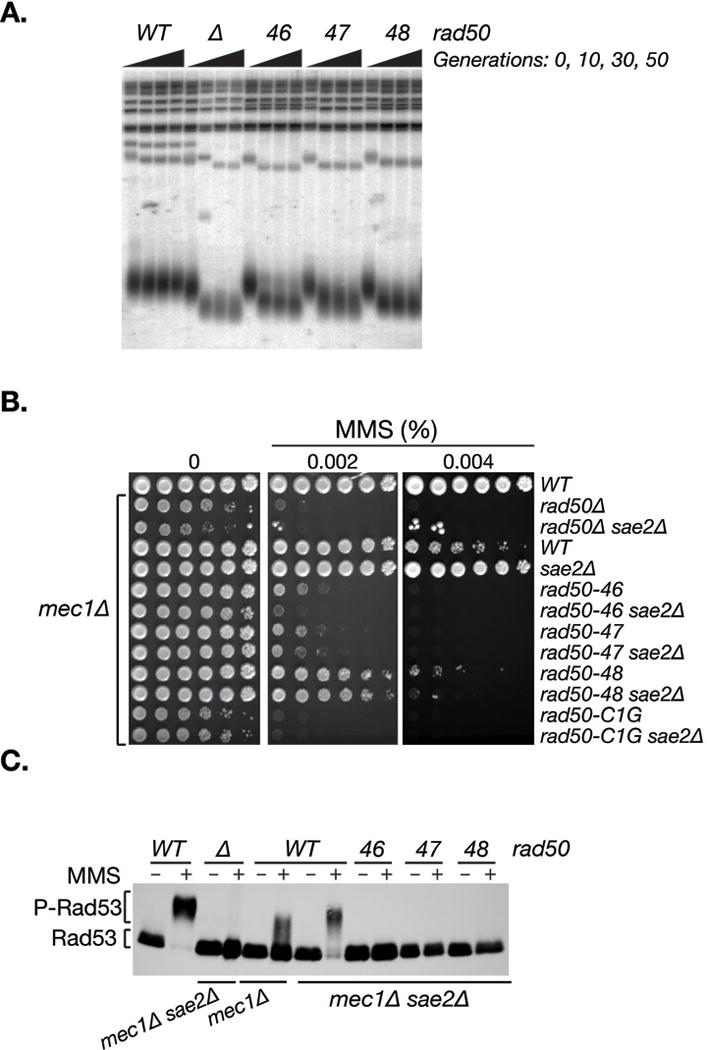
A. Telomere lengths of wild-type and rad50hook mutants after 10, 30 and 50 generations of growth at 30°C. Heterozygote diploids (RAD50/ rad50hook) were included as 0 generations of growth. B. Cell survival of rad50hook mutants in a Mec1-deficient background. All strains below the wild-type strain (top row) were mec1Δ sml1Δ. C. Tel1-dependent Rad53 phosphorylation in Mec1-deficient cells upon MMS treatment (+) assessed by western blot. The migration levels of the non-phosphorylated (Rad53) and phosphorylated form (P-Rad53) are indicated. Rad50 genotypes are given above the blot and the Mec1 and Sae2 status (either wild-type or deleted) below.
