Figure 5. Meiotic DSBs processing is impaired in rad50-46 and rad50-47 but not rad50-48.
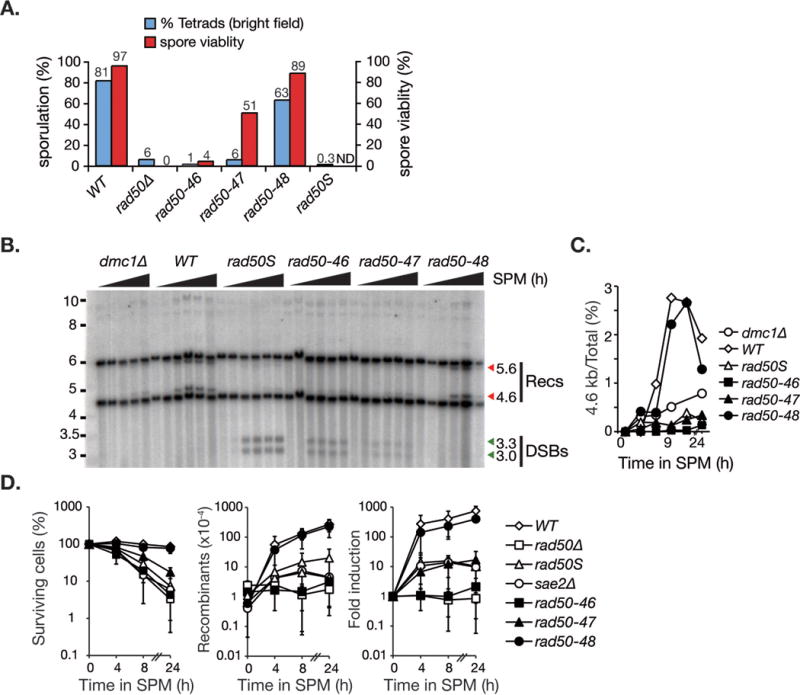
A. Sporulation efficiency (in blue) and spore viability (in red) of the indicated genotypes were assessed in SK1 homozygot diploid cells after 48 hours sporulation. The sporulation efficiency was calculated as the percentage of asci among total number of cells (% tetrads) and graphically illustrated (% sporulation, y-axis on the left). Spore viability was determined by tetrad dissection of at least 30 tetrads (% spore viability, y-axis on the right). Spore viability for rad50S/S was not determined (ND). B. Meiotic DSB formation and repair by meiotic recombination at the HIS4-LEU2 hotspot by southern blot. The migration level of the crossover recombinant fragments (Recs, recombinants; 5.6 kb and 4.6 kb, red arrows) above and below the parental band (Hunter and Kleckner, 2001; Schwacha and Kleckner, 1997) and the unprocessed 3.3 kb and 3.0 kb meiotic double strand break fragments (DSB, green arrows) are denoted. Cells were cultivated in sporulation media (SPM) for 0, 3, 6, 9 and 24 (dmc1Δ) or for 0, 3, 6, 9, 12 and 24 hours (WT, rad50S, rad50-46, rad50-47 and rad50-48). C. Relative signal intensities of the 4.6 kb recombinant fragment versus total counts per lane is shown on the right.
