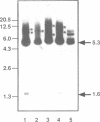
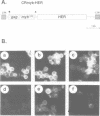
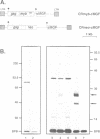
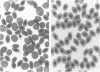
Abstract
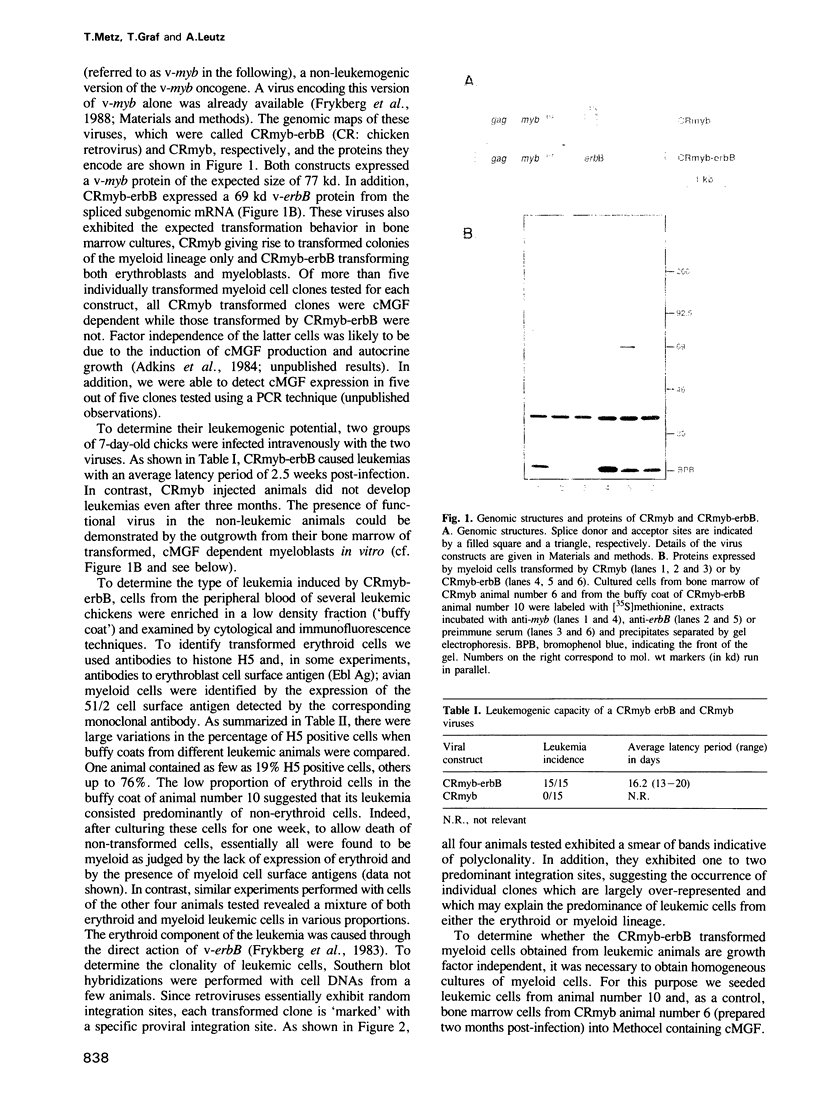
A non-leukemogenic version of the v-myb oncogene causes in vitro transformation of avian myeloblasts, which are dependent on chicken myelomonocytic growth factor (cMGF). We have shown that this version of v-myb, when combined with the erythroleukemia-inducing v-erbB oncogene, is capable of causing a mixed myeloid and erythroid leukemia. Myeloid leukemic cells transformed by this construct produce cMGF. To test whether autocrine growth stimulation via cMGF is the essential contribution of the tyrosine kinase oncogene v-erbB in avian myeloid leukemogenesis we constructed another retrovirus containing both the non-leukemogenic v-myb and the cMGF cDNA. This virus induced myeloid leukemia at high efficiency. In a third construct we combined v-myb with the human EGF-receptor gene. Myeloid cells transformed by this construct could be stimulated to grow by the addition of cMGF or EGF. Growth stimulation with EGF was blocked by a cMGF antiserum indicating that activation of a normal tyrosine kinase-type receptor induces cMGF expression but does not bypass the cMGF requirement. We conclude that cMGF plays a key role in the growth regulation of normal and transformed avian myeloid cells.
Full text
PDF
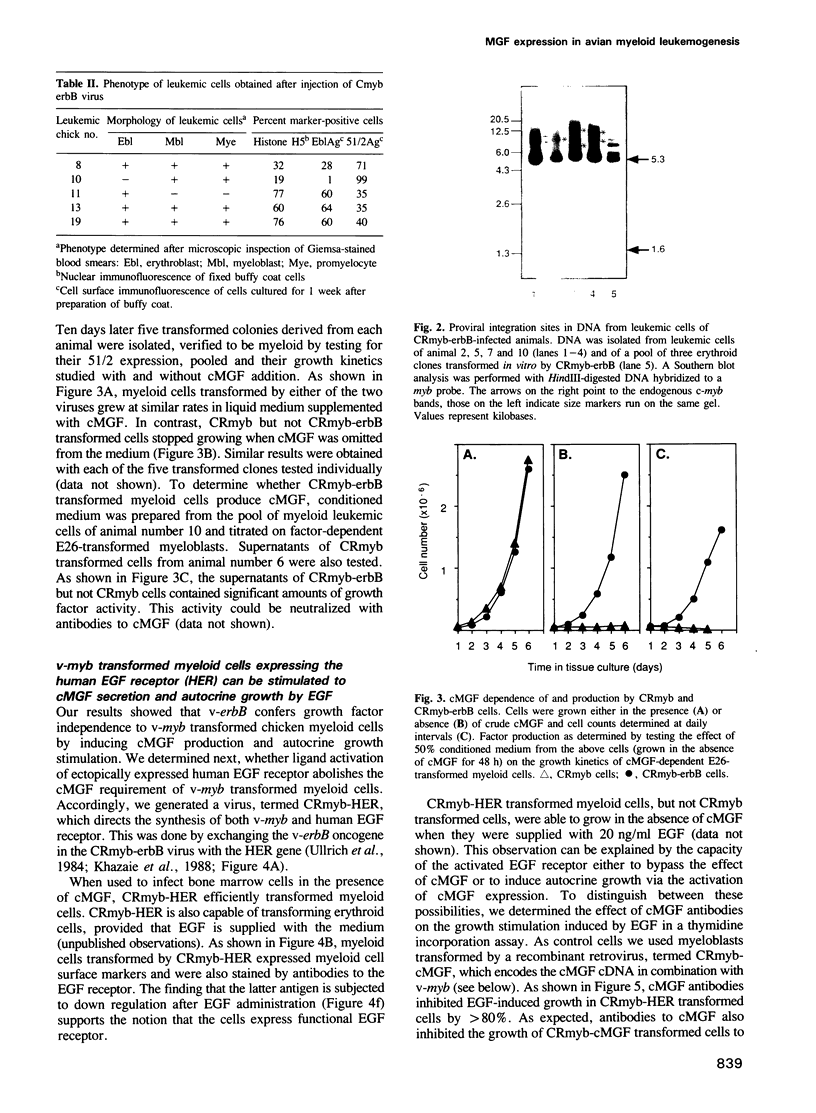



Images in this article
Selected References
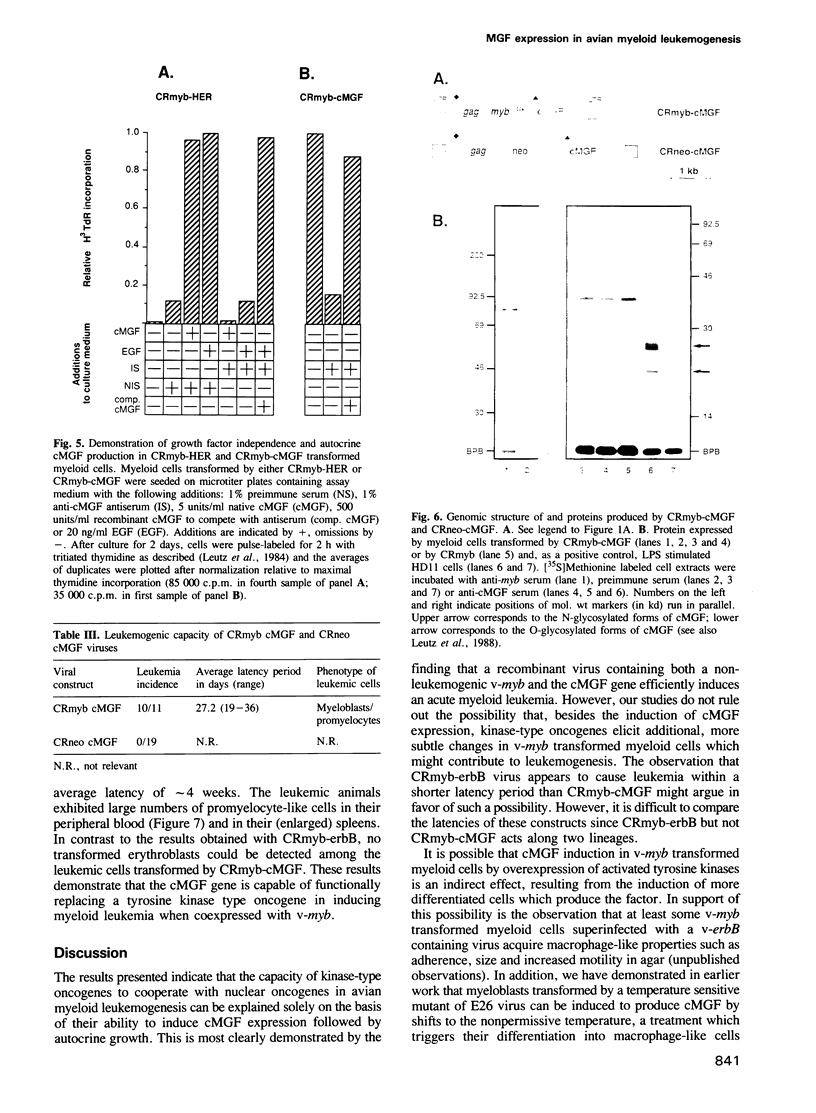
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adkins B., Leutz A., Graf T. Autocrine growth induced by src-related oncogenes in transformed chicken myeloid cells. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):439–445. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90451-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beug H., Doederlein G., Freudenstein C., Graf T. Erythroblast cell lines transformed by a temperature-sensitive mutant of avian erythroblastosis virus: a model system to study erythroid differentiation in vitro. J Cell Physiol Suppl. 1982;1:195–207. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041130427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
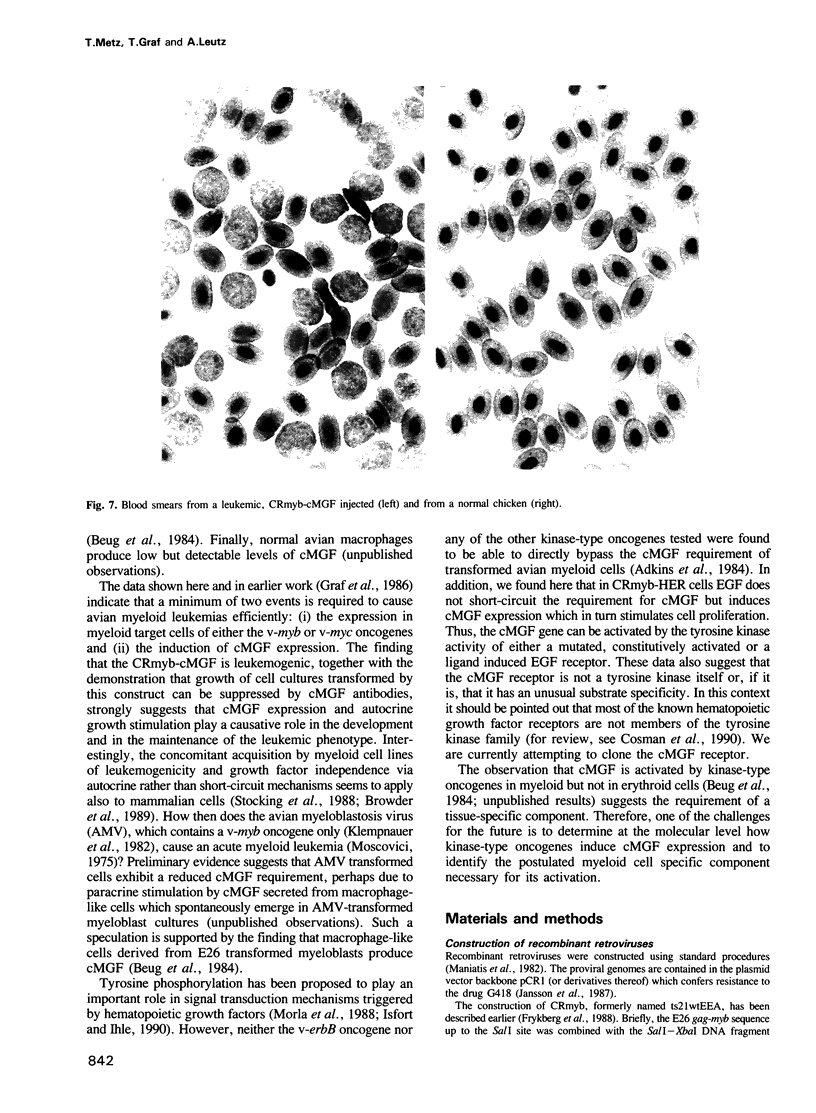
- Beug H., Hayman M. J., Graf T. Myeloblasts transformed by the avian acute leukemia virus E26 are hormone-dependent for growth and for the expression of a putative myb-containing protein, p135 E26. EMBO J. 1982;1(9):1069–1073. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01298.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beug H., Leutz A., Kahn P., Graf T. Ts mutants of E26 leukemia virus allow transformed myeloblasts, but not erythroblasts or fibroblasts, to differentiate at the nonpermissive temperature. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):579–588. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90465-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beug H., von Kirchbach A., Döderlein G., Conscience J. F., Graf T. Chicken hematopoietic cells transformed by seven strains of defective avian leukemia viruses display three distinct phenotypes of differentiation. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):375–390. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90057-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Browder T. M., Dunbar C. E., Nienhuis A. W. Private and public autocrine loops in neoplastic cells. Cancer Cells. 1989 Sep;1(1):9–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi O. R., Trainor C., Graf T., Beug H., Engel J. D. A single amino acid substitution in v-erbB confers a thermolabile phenotype to ts167 avian erythroblastosis virus-transformed erythroid cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1751–1759. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cosman D., Lyman S. D., Idzerda R. L., Beckmann M. P., Park L. S., Goodwin R. G., March C. J. A new cytokine receptor superfamily. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Jul;15(7):265–270. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90051-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frykberg L., Metz T., Brady G., Introna M., Beug H., Vennström B., Graf T. A point mutation in the DNA binding domain of the v-myb oncogene of E26 virus confers temperature sensitivity for transformation of myelomonocytic cells. Oncogene Res. 1988;3(4):313–322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frykberg L., Palmieri S., Beug H., Graf T., Hayman M. J., Vennström B. Transforming capacities of avian erythroblastosis virus mutants deleted in the erbA or erbB oncogenes. Cell. 1983 Jan;32(1):227–238. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90513-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazzolo L., Moscovici C., Moscovici M. G., Samarut J. Response of hemopoietic cells to avian acute leukemia viruses: effects on the differentiation of the target cells. Cell. 1979 Mar;16(3):627–638. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90036-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf T., Beug H. Avian leukemia viruses: interaction with their target cells in vivo and in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Nov 17;516(3):269–299. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(78)90011-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf T. Two types of target cells for transformation with avian myelocytomatosis virus. Virology. 1973 Aug;54(2):398–413. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90152-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf T., von Kirchbach A., Beug H. Characterization of the hematopoietic target cells of AEV, MC29 and AMV avian leukemia viruses. Exp Cell Res. 1981 Feb;131(2):331–343. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(81)90236-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf T., von Weizsaecker F., Grieser S., Coll J., Stehelin D., Patschinsky T., Bister K., Bechade C., Calothy G., Leutz A. v-mil induces autocrine growth and enhanced tumorigenicity in v-myc-transformed avian macrophages. Cell. 1986 May 9;45(3):357–364. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90321-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayman M. J., Ramsay G. M., Savin K., Kitchener G., Graf T., Beug H. Identification and characterization of the avian erythroblastosis virus erbB gene product as a membrane glycoprotein. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):579–588. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90477-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Introna M., Golay J., Frampton J., Nakano T., Ness S. A., Graf T. Mutations in v-myb alter the differentiation of myelomonocytic cells transformed by the oncogene. Cell. 1990 Dec 21;63(6):1289–1297. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90424-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isfort R. J., Ihle J. N. Multiple hematopoietic growth factors signal through tyrosine phosphorylation. Growth Factors. 1990;2(2-3):213–220. doi: 10.3109/08977199009071507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansson M., Beug H., Gray C., Graf T., Vennström B. Defective v-erbB genes can be complemented by v-erbA in erythroblast and fibroblast transformation. Oncogene. 1987 May;1(2):167–173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn P., Adkins B., Beug H., Graf T. src- and fps-containing avian sarcoma viruses transform chicken erythroid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):7122–7126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.7122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khazaie K., Dull T. J., Graf T., Schlessinger J., Ullrich A., Beug H., Vennström B. Truncation of the human EGF receptor leads to differential transforming potentials in primary avian fibroblasts and erythroblasts. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3061–3071. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03171.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klempnauer K. H., Gonda T. J., Bishop J. M. Nucleotide sequence of the retroviral leukemia gene v-myb and its cellular progenitor c-myb: the architecture of a transduced oncogene. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):453–463. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90138-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld S., Beug H., Doederlein G., Graf T. Detection of avian hematopoietic cell surface antigens with monoclonal antibodies to myeloid cells. Their distribution on normal and leukemic cells of various lineages. Exp Cell Res. 1983 Feb;143(2):383–394. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(83)90065-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leutz A., Beug H., Graf T. Purification and characterization of cMGF, a novel chicken myelomonocytic growth factor. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3191–3197. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02278.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leutz A., Beug H., Walter C., Graf T. Hematopoietic growth factor glycosylation. Multiple forms of chicken myelomonocytic growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 15;263(8):3905–3911. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leutz A., Damm K., Sterneck E., Kowenz E., Ness S., Frank R., Gausepohl H., Pan Y. C., Smart J., Hayman M. Molecular cloning of the chicken myelomonocytic growth factor (cMGF) reveals relationship to interleukin 6 and granulocyte colony stimulating factor. EMBO J. 1989 Jan;8(1):175–181. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03362.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLeod D. L., Shreeve M. M., Axelrad A. A. Improved plasma culture system for production of erythrocytic colonies in vitro: quantitative assay method for CFU-E. Blood. 1974 Oct;44(4):517–534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morla A. O., Schreurs J., Miyajima A., Wang J. Y. Hematopoietic growth factors activate the tyrosine phosphorylation of distinct sets of proteins in interleukin-3-dependent murine cell lines. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2214–2218. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscovici C. Leukemic transformation with avian myeloblastosis virus: present status. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1975;71:79–101. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-66193-8_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ness S. A., Beug H., Graf T. v-myb dominance over v-myc in doubly transformed chick myelomonocytic cells. Cell. 1987 Oct 9;51(1):41–50. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90008-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radke K., Beug H., Kornfeld S., Graf T. Transformation of both erythroid and myeloid cells by E26, an avian leukemia virus that contains the myb gene. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(3 Pt 2):643–653. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90320-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stocking C., Löliger C., Kawai M., Suciu S., Gough N., Ostertag W. Identification of genes involved in growth autonomy of hematopoietic cells by analysis of factor-independent mutants. Cell. 1988 Jun 17;53(6):869–879. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)90329-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Coussens L., Hayflick J. S., Dull T. J., Gray A., Tam A. W., Lee J., Yarden Y., Libermann T. A., Schlessinger J. Human epidermal growth factor receptor cDNA sequence and aberrant expression of the amplified gene in A431 epidermoid carcinoma cells. 1984 May 31-Jun 6Nature. 309(5967):418–425. doi: 10.1038/309418a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vennström B., Bishop J. M. Isolation and characterization of chicken DNA homologous to the two putative oncogenes of avian erythroblastosis virus. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):135–143. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90383-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]