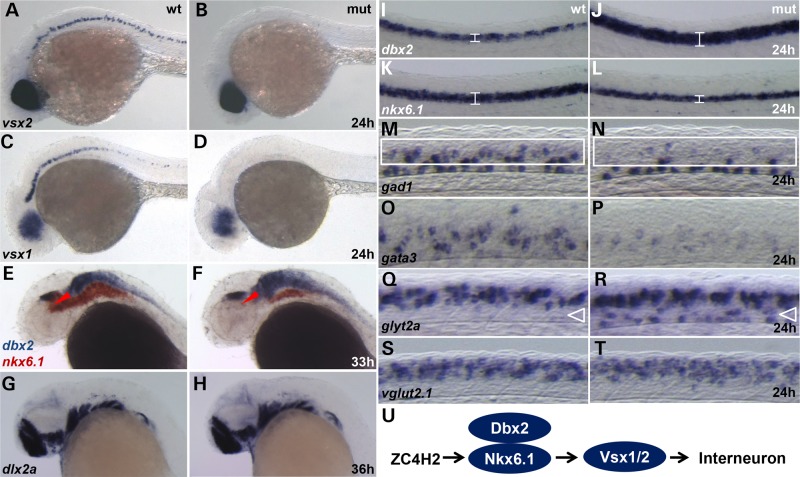
Figure 5.
Whole-mount in situ hybridization for neural markers in wild-type sibling (wt) and zc4h2 KO mutant (mut) zebrafish. (A–D) At 24 h, expression of vsx2 and vsx1, markers for V2a interneurons and V2a/b precursors, respectively, was significantly reduced in the brain and spinal cord of mutants. (E and F) At 33 hpf, expression of dbx2 (blue) was increased and expression of nkx6.1 (red) was decreased in the midbrain tegmentum (*). and hindbrain of mutants. (G and H) At 35 hpf, expression of dlx2a, a marker of forebrain GABAergic precursors, was unaffected in mutants. (I–L) At 24 hpf, expression of dbx2 was increased and expression of nkx6.1 was decreased (brackets) in the spinal cord of mutants. (M and N) Expression of gad1, a marker for GABAergic neurons, was decreased in V2 interneuron territories of the mutant spinal cord (White rectangles). (O and P) gata3 expression, a marker for V2b inhibitory interneurons, was dramatically reduced in the mutant spinal cord. (Q and R) glyt2a, a marker for glycinergic neurons, was ectopically expressed in the mutant spinal cord. (S and T) vglut2.1 expression, a marker for glutamatergic excitatory neurons, was unaffected in zc4h2 homozygous mutant zebrafish. (U) Model for Zc4h2 function in zebrafish interneuron specification.