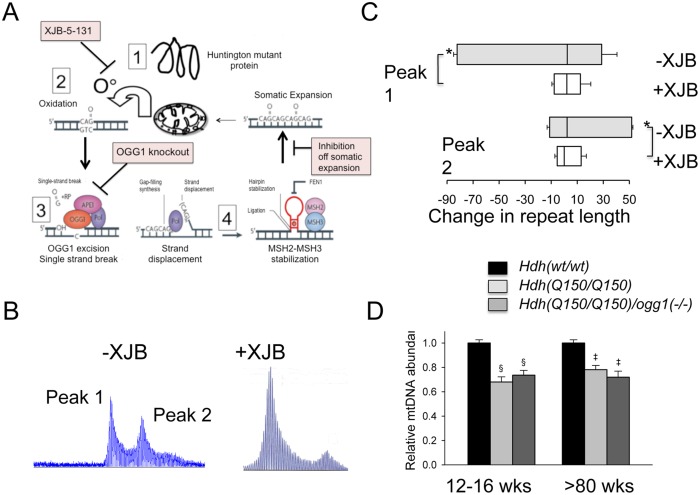
Fig 5. Pharmacological intervention suppresses oxidative DNA damage and somatic mutation in vivo.
XJB-5-131 synthesis [51] and administration is as previously described [36]. (A) OGG1 and XJB-5-131 act in the same expansion pathway. Schematic diagram for the mechanism of somatic expansion (adapted from [1]), and the point of inhibition by XJB-5-131 or loss of OGG1. XJB-5-131 reduces oxidative DNA damage (the substrate for OGG1) and loss of OGG1 reduces base excision and single strand break intermediates for expansion by BER. (B) Representative examples of GeneScan analysis of Hdh(Q150/Q150)/ogg1(+/+) striatum of animals untreated or treated with XJB-5-131. (C) Quantification of repeat changes ± standard deviation for animals age 21–30 weeks. The somatic expansions in XJB-5-131-treated Hdh(Q150/Q150)/ogg1(+/+) animals are smaller than in untreated animals in the striatum. N = 6 per group (with and without XJB-5-131 treatment) *p<0.001. (D) Levels of mtDNA abundance in cerebral cortex of Hdh(wt/wt), Hdh(Q150/Q150)/ogg1(+/+) and Hdh(Q150/Q150)/ogg1(-/-) animals at 12–16 weeks (n = 6) and >80 weeks of age (n = 6–9). §p<0.0001 versus 12–16 weeks WT and ‡p<0.0001 versus >80 weeks WT.