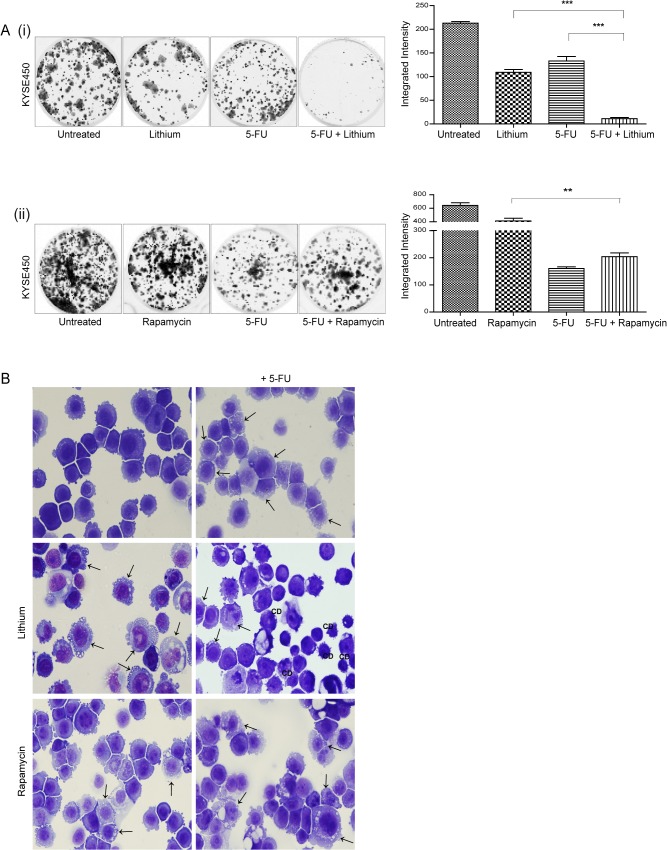
Fig 2. Assessment of the effect of autophagy inducers on chemosensitivity in human esophageal cancer cells.
KYSE450 cells were treated with lithium chloride (lithium) (30 mM) or rapamycin (300 nM) alone or in combination with 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) (40 μM) for 48 hours. (A) Viable cells following treatment with either lithium (i) or rapamycin (ii) alone or in combination with 5-FU for 48 hours were counted and equal numbers reseeded in triplicate, in the absence of drug. Cells were allowed to grow for 14 days, then were fixed and stained and colonies quantified using the Odyssey Infrared Imaging System (Li-COR). Data is presented graphically as the mean +/- SEM of three independent experiments. Asterisks indicate a significant difference in the number of colonies formed in combination treated cells compared to single agent treated cells (*** p < 0.0005, ** p < 0.005) (unpaired t-test). (B) Morphological features of KYSE450 cells were examined following treatment for 48 hours. Panels to the left show the morphology induced in response to lithium or rapamycin alone, panels to the right show morphology with the addition of 5-FU. Arrows indicate the accumulation of autophagic vesicles in lithium, rapamycin, 5-FU and combination treated cells. CD denotes the presence of a non-apoptotic cell death morphology (Magnification 40x).