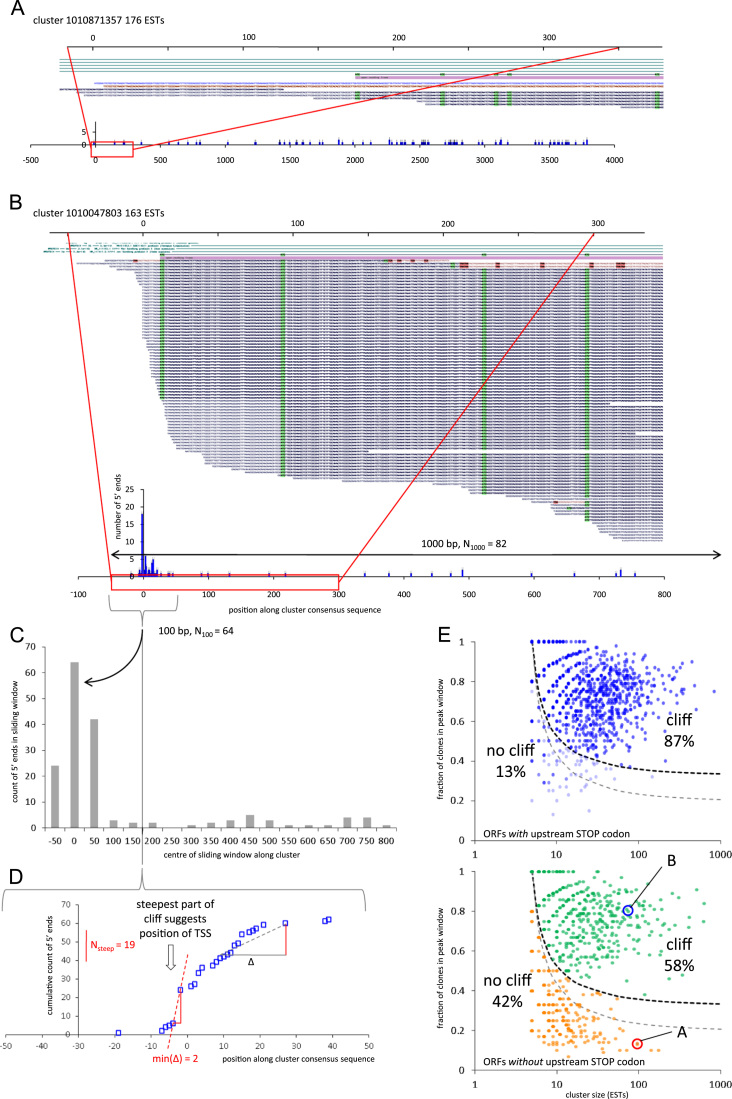
Fig. 3.
‘Cliff’ algorithm for confirming full-ORF status. A concentration of the positions of 5′ ends of clones in assembled clusters identifies the likely start of transcription, which is, by definition, upstream of the start of translation. (A) Cluster with 176 ESTs showing truncated open reading frame and no start of transcription. (B) Cluster with 163 ESTs showing ‘cliff’ of 5′ end positions likely containing the start of transcription. (C) Cliff finding: histogram of numbers of 5′ ends in sliding windows of 100 bp determined every 50 bp along 1000 bp of cluster, and used to find the ‘peak’ region of 5′ end density (N100/N1000). (D) Cliff steepness and transcription start site (TSS) prediction: analysis of cumulative 5′ end count across ‘peak’ 100 bp window, used to find the steepest part of the cliff for a determined fraction of reads in the window. (E) Cliff threshold: plots to test the cluster size dependent term for the limiting value N100/N1000, used to determine the presence of a ‘cliff’ and hence the likely start of translation (see text). The heavy dashed line follows the form where Z is the clusters size (number of ESTs). Individual EST clusters (spots) are plotted according to their ‘peak’ of 5′ ends (N100/N1000) on the y-axis, and cluster size (Z) on the x-axis; those falling right and above of the limiting curve are assumed likely to contain sufficient cliff and the start of transcription. (Upper panel) Verification of cliff algorithm: (blue dots) clusters with upstream stop codon confirming open reading frame, showing score is a good predictor of full-ORF status. (Lower panel) Clone selection with cliff algorithm: clusters without upstream stop codon, showing clear bimodal distribution with cluster consensus sequences assumed full-ORF (green) and those assumed truncated (orange). Spots corresponding to the example genes in panels A and B are marked. The light dashed line shows the curve used to determine the proportion of 5′ ends in the peak window used to look for the steepest section of the cliff (see D).