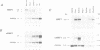Abstract
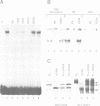
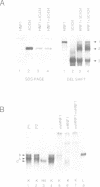
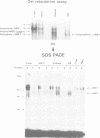
vHNF1 and HNF1 are two nuclear proteins that bind to an essential element in the promoter proximal sequences of albumin and of many other liver-specific genes. HNF1 predominates in hepatocytes but is absent in dedifferentiated hepatoma cells. These cells contain vHNF1 but fail to express most of the liver traits. In the present work we have isolated cDNA clones for vHNF1 and found that it is a homeoprotein homologous to HNF1 in regions important for DNA binding. Unexpectedly, vHNF1 transactivated the albumin promoter in transfection experiments. Like the HNF1 mRNA, the vHNF1 message was found in kidney, liver and intestine although in different proportions. The fact that vHNF1 and HNF1 readily form heterodimers in vitro and the biochemical characterization of vHNF1/HNF1 heterodimers in nuclear extracts of kidney, liver and several cell lines, strongly argue that such heterodimers exist in vivo. Our results raise the possibility that heterodimerization between homeoproteins could be a common phenomenon in higher eukaryotes, which may have implications in the regulatory network sustained between these factors.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Affolter M., Schier A., Gehring W. J. Homeodomain proteins and the regulation of gene expression. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;2(3):485–495. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(90)90132-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach I., Galcheva-Gargova Z., Mattei M. G., Simon-Chazottes D., Guénet J. L., Cereghini S., Yaniv M. Cloning of human hepatic nuclear factor 1 (HNF1) and chromosomal localization of its gene in man and mouse. Genomics. 1990 Sep;8(1):155–164. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90238-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumhueter S., Courtois G., Crabtree G. R. A variant nuclear protein in dedifferentiated hepatoma cells binds to the same functional sequences in the beta fibrinogen gene promoter as HNF-1. EMBO J. 1988 Aug;7(8):2485–2493. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03095.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumhueter S., Mendel D. B., Conley P. B., Kuo C. J., Turk C., Graves M. K., Edwards C. A., Courtois G., Crabtree G. R. HNF-1 shares three sequence motifs with the POU domain proteins and is identical to LF-B1 and APF. Genes Dev. 1990 Mar;4(3):372–379. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.3.372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benezra R., Davis R. L., Lockshon D., Turner D. L., Weintraub H. The protein Id: a negative regulator of helix-loop-helix DNA binding proteins. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):49–59. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90214-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cereghini S., Blumenfeld M., Yaniv M. A liver-specific factor essential for albumin transcription differs between differentiated and dedifferentiated rat hepatoma cells. Genes Dev. 1988 Aug;2(8):957–974. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.8.957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cereghini S., Yaniv M., Cortese R. Hepatocyte dedifferentiation and extinction is accompanied by a block in the synthesis of mRNA coding for the transcription factor HNF1/LFB1. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2257–2263. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07396.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chouard T., Blumenfeld M., Bach I., Vandekerckhove J., Cereghini S., Yaniv M. A distal dimerization domain is essential for DNA-binding by the atypical HNF1 homeodomain. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 11;18(19):5853–5863. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.19.5853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran T., Franza B. R., Jr Fos and Jun: the AP-1 connection. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):395–397. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90024-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deschatrette J., Weiss M. C. Characterization of differentiated and dedifferentiated clones from a rat hepatoma. Biochimie. 1974;56(11-12):1603–1611. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(75)80286-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dollé P., Izpisúa-Belmonte J. C., Falkenstein H., Renucci A., Duboule D. Coordinate expression of the murine Hox-5 complex homoeobox-containing genes during limb pattern formation. Nature. 1989 Dec 14;342(6251):767–772. doi: 10.1038/342767a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dranginis A. M. Binding of yeast a1 and alpha 2 as a heterodimer to the operator DNA of a haploid-specific gene. Nature. 1990 Oct 18;347(6294):682–685. doi: 10.1038/347682a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng D. F., Johnson M. S., Doolittle R. F. Aligning amino acid sequences: comparison of commonly used methods. J Mol Evol. 1984;21(2):112–125. doi: 10.1007/BF02100085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiering S., Northrop J. P., Nolan G. P., Mattila P. S., Crabtree G. R., Herzenberg L. A. Single cell assay of a transcription factor reveals a threshold in transcription activated by signals emanating from the T-cell antigen receptor. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1823–1834. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finney M. The homeodomain of the transcription factor LF-B1 has a 21 amino acid loop between helix 2 and helix 3. Cell. 1990 Jan 12;60(1):5–6. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90708-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frain M., Swart G., Monaci P., Nicosia A., Stämpfli S., Frank R., Cortese R. The liver-specific transcription factor LF-B1 contains a highly diverged homeobox DNA binding domain. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):145–157. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90877-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrell J., Modolell J. The Drosophila extramacrochaetae locus, an antagonist of proneural genes that, like these genes, encodes a helix-loop-helix protein. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):39–48. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90213-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehring W. J. Homeo boxes in the study of development. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1245–1252. doi: 10.1126/science.2884726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goutte C., Johnson A. D. a1 protein alters the DNA binding specificity of alpha 2 repressor. Cell. 1988 Mar 25;52(6):875–882. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90429-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III in DNA sequence analysis. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:156–165. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55014-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland P. W., Hogan B. L. Expression of homeo box genes during mouse development: a review. Genes Dev. 1988 Jul;2(7):773–782. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.7.773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N. Transcriptional regulation by dimerization: two sides to an incestuous relationship. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):9–11. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90207-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keleher C. A., Goutte C., Johnson A. D. The yeast cell-type-specific repressor alpha 2 acts cooperatively with a non-cell-type-specific protein. Cell. 1988 Jun 17;53(6):927–936. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)90449-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelleher R. J., 3rd, Flanagan P. M., Kornberg R. D. A novel mediator between activator proteins and the RNA polymerase II transcription apparatus. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1209–1215. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90685-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M., Hoey T. Homeobox proteins as sequence-specific transcription factors. Cell. 1988 Nov 18;55(4):537–540. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90209-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewin B. Commitment and activation at pol II promoters: a tail of protein-protein interactions. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1161–1164. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90675-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis E. B. A gene complex controlling segmentation in Drosophila. Nature. 1978 Dec 7;276(5688):565–570. doi: 10.1038/276565a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtsteiner S., Schibler U. A glycosylated liver-specific transcription factor stimulates transcription of the albumin gene. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1179–1187. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90055-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Goodbourn S., Fischer J. A. Regulation of inducible and tissue-specific gene expression. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1237–1245. doi: 10.1126/science.3296191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicosia A., Monaci P., Tomei L., De Francesco R., Nuzzo M., Stunnenberg H., Cortese R. A myosin-like dimerization helix and an extra-large homeodomain are essential elements of the tripartite DNA binding structure of LFB1. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1225–1236. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90687-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott M. O., Sperling L., Herbomel P., Yaniv M., Weiss M. C. Tissue-specific expression is conferred by a sequence from the 5' end of the rat albumin gene. EMBO J. 1984 Nov;3(11):2505–2510. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02164.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otting G., Qian Y. Q., Billeter M., Müller M., Affolter M., Gehring W. J., Wüthrich K. Protein--DNA contacts in the structure of a homeodomain--DNA complex determined by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy in solution. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3085–3092. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07505.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. How eukaryotic transcriptional activators work. Nature. 1988 Oct 20;335(6192):683–689. doi: 10.1038/335683a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qian Y. Q., Billeter M., Otting G., Müller M., Gehring W. J., Wüthrich K. The structure of the Antennapedia homeodomain determined by NMR spectroscopy in solution: comparison with prokaryotic repressors. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):573–580. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90040-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulz B., Banuett F., Dahl M., Schlesinger R., Schäfer W., Martin T., Herskowitz I., Kahmann R. The b alleles of U. maydis, whose combinations program pathogenic development, code for polypeptides containing a homeodomain-related motif. Cell. 1990 Jan 26;60(2):295–306. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90744-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M. P., Tamkun J. W., Hartzell G. W., 3rd The structure and function of the homeodomain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jul 28;989(1):25–48. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(89)90033-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl G., Struhl K., Macdonald P. M. The gradient morphogen bicoid is a concentration-dependent transcriptional activator. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1259–1273. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90062-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theill L. E., Castrillo J. L., Wu D., Karin M. Dissection of functional domains of the pituitary-specific transcription factor GHF-1. Nature. 1989 Dec 21;342(6252):945–948. doi: 10.1038/342945a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tronche F., Rollier A., Bach I., Weiss M. C., Yaniv M. The rat albumin promoter: cooperation with upstream elements is required when binding of APF/HNF1 to the proximal element is partially impaired by mutation or bacterial methylation. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):4759–4766. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.4759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tronche F., Rollier A., Herbomel P., Bach I., Cereghini S., Weiss M., Yaniv M. Anatomy of the rat albumin promoter. Mol Biol Med. 1990 Apr;7(2):173–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B. Transcription elements and factors of RNA polymerase B promoters of higher eukaryotes. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1988;23(2):77–120. doi: 10.3109/10409238809088317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yee C., Krishnan-Hewlett I., Baker C. C., Schlegel R., Howley P. M. Presence and expression of human papillomavirus sequences in human cervical carcinoma cell lines. Am J Pathol. 1985 Jun;119(3):361–366. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]