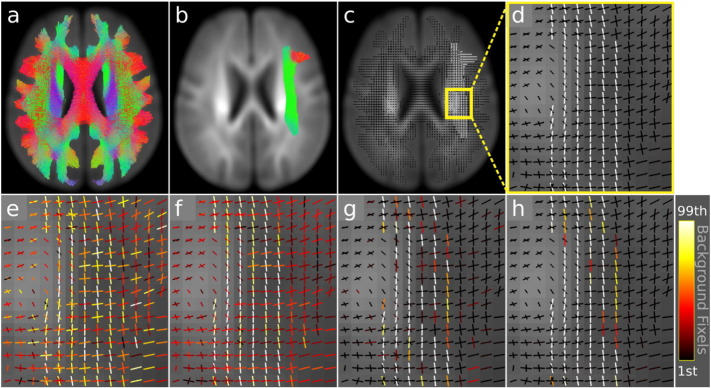
Fig. 3.
Illustrative example. a) Whole-brain probabilistic tractogram computed on the group-average FOD template. Streamlines were used to derive fixel–fixel connectivity for smoothing and enhancement. Streamlines are coloured by direction (red: left–right, blue: inferior–superior, green: anterior–posterior). b) A tract-of-interest, the arcuate fasciculus, was extracted from the whole-brain tractogram in a (note that only streamlines belonging to the slice are shown). c) Individual fixels belonging to the arcuate fasciculus were identified based on streamline visitation. All arcuate fixels were assigned a ‘signal’ of one. d) Zoomed in region of the ‘signal only’ image in c showing the arcuate fasciculus fixels in white and background (zero) fixels in black. e) Signal + noise image after adding Gaussian noise (signal-to-noise of 2) to the signal only image in d. f) Connectivity-based smoothing of e. g) CFE of e. h) Both connectivity-based smoothing and CFE of e. To best visualise the separation of signal from background, all images e–f are windowed based on the 1st to 99th percentile of the background fixel values.