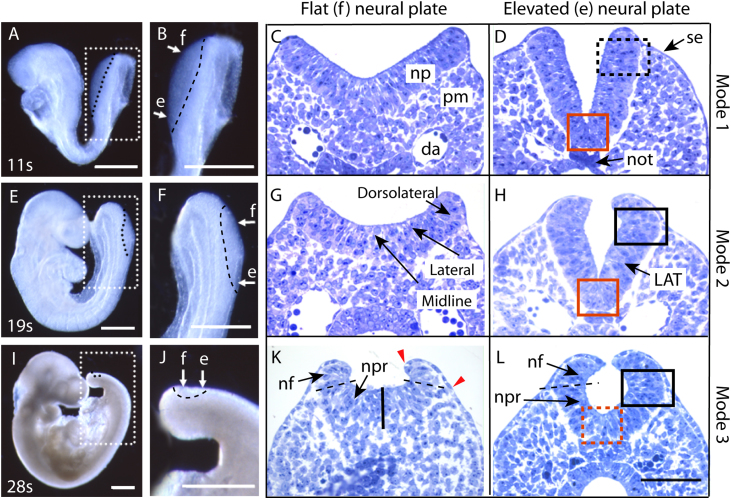
Fig. 1.
Embryo and posterior neuropore (PNP) morphology at successive stages of mouse spinal neurulation. (A, B, E, F, I, J) Whole embryos at E8.5 (A), E9.5 (E) and E10 (I) and enlarged views of the caudal region (B, F, J; white dotted boxes in A, E, I). The PNP (black dotted lines) shortens progressively as development proceeds. Arrows indicate level of sections through flat (f) and elevated (e) neural plate. (C, D, G, H, K, L) Transverse 2.5 μm thick plastic sections through the PNP showing transition from flat (C, G, K) to elevated (D, H, L) neural folds. At E8.5 (C, D; Mode 1), bending is solely at MHP (red box); at E9.5 (G, H; Mode 2), both MHP and DLHPs (black box) are present, with non-bending lateral neural plate (LAT) in between; at E10 (K, L; Mode 3), only DLHP bending occurs. Dorsolateral non-bending neural plate at Mode 1 (dotted black box, D) and midline non-bending neural plate at Mode 3 (dotted red box, L) were also analysed. Dashed lines (K, L): boundary between neural fold (nf) and neuroepithelium outside neural fold (npr); solid line (K): midline. Red arrowheads (K): surface ectoderm juxtaposed to neuroepithelium of the neural fold. Abbreviations: da, dorsal aorta; not, notochord; np, neural plate; pm, paraxial mesoderm; s, somite number. Scale bars: A,B,E,F,I,J: 0.5 mm; L (for all sections): 0.1 mm.