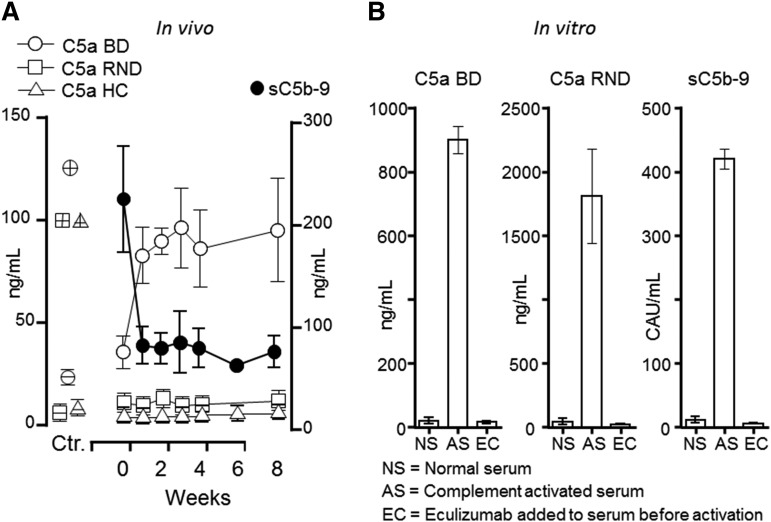
Figure 1.
Effect of eculizumab on C5a and sC5b-9 generation in vivo and in vitro. (A) Plasma samples from 3 patients with aHUS were obtained at baseline (week 0) and during 8 weeks after the start of eculizumab treatment. C5a measured by the BD Biosience ELISA (BD) showed an abrupt increase in all 3 patients after the start of eculizumab, whereas no increase was seen in the C5a assays from RND Systems or HC. The controls (Ctr.) are shown to the left: negative controls (open circle, square and triangle symbols corresponding to those given for the kits, but with an inner horizontal line) represent 3 normal human EDTA plasma samples. Positive controls (similar open symbols as for the 3 kits, but with inner horizontal and vertical lines) represent C5a for the BD and RND kit and C5desarg for the Hycult kit. As expected, sC5b-9 (BD) decreased immediately after eculizumab treatment was started (right y-axis). (B) A pool of normal human serum (NS) was activated with heat aggregated IgG (AS), revealing an excessive increase in C5a both in the BD and RND kits, as well as in sC5b9. The latter was measured by a singleplex assay using an international complement activation standard given in complement activation units (CAU) per milliliter.8 Addition of eculizumab (EC) to the serum before activation completely abrogated C5a formation as detected in both the BD and the RND assay, as well sC5b-9 formation.