FIGURE 6.
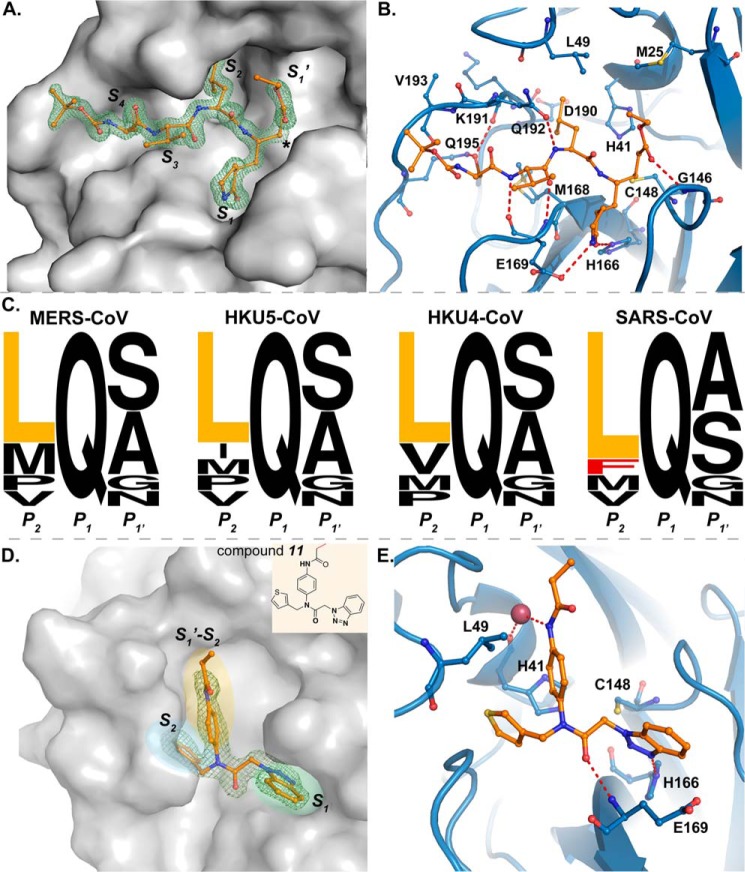
X-ray crystal structure of MERS-CoV 3CLpro in complex with inhibitors. A, solvent-accessible surface (gray-shaded surface) of MERS-CoV 3CLpro and compound 6 complex. Compound 6 is displayed in ball and stick model with atoms colored as follows: carbons (orange), nitrogens (blue), and oxygens (red). Electron density associated with compound 6 is shown as an Fo − Fc electron density difference map contoured to 3σ (green mesh). Substrate binding pockets S4-S′1 are labeled, where asterisk indicates the electrophilic carbon of compound 6 that forms a C–S covalent bond with the active site cysteine Cys-148. B, MERS-CoV 3CLpro and compound 6 complex with the MERS-CoV 3CLpro backbone represented as a ribbon model and relevant amino acids that interact with compound 6 represented as ball and sticks. MERS-CoV 3CLpro carbon atoms are colored blue, and compound 6 carbon atoms are colored orange. Nitrogen atoms are colored blue, and oxygen atoms are colored red. Catalytic residues Cys-148 and His-41 are also shown. Hydrogen bonds are depicted as red dashed lines. C, sequence logos showing amino acid conservation for the 11 polyprotein cleavage sites of different 3CLpro enzymes (MERS-CoV, HKU5-CoV, HKU4-CoV, and SARS-CoV), generated using the WebLogo server (63). Residues P2-P′1 are shown. Height of each letter corresponds to the amino acid conservation at that position. D, solvent-accessible surface (gray-shaded surface) of MERS-CoV 3CLpro and compound 11 complex. Compound 11 is displayed in ball and stick model. Electron density associated with compound 11 is shown as a 2Fo − Fc electron density difference map contoured to 1.5σ (green mesh). Functional groups of compound 11 with their corresponding binding pockets are highlighted in yellow, green, and blue ellipses. Chemical structure of compound 11 is shown in the inset. E, interactions between MERS-CoV 3CLpro and compound 11 are illustrated. Catalytic residues Cys-148 and His-41 are also shown. Hydrogen bonds are depicted as red dashed lines.