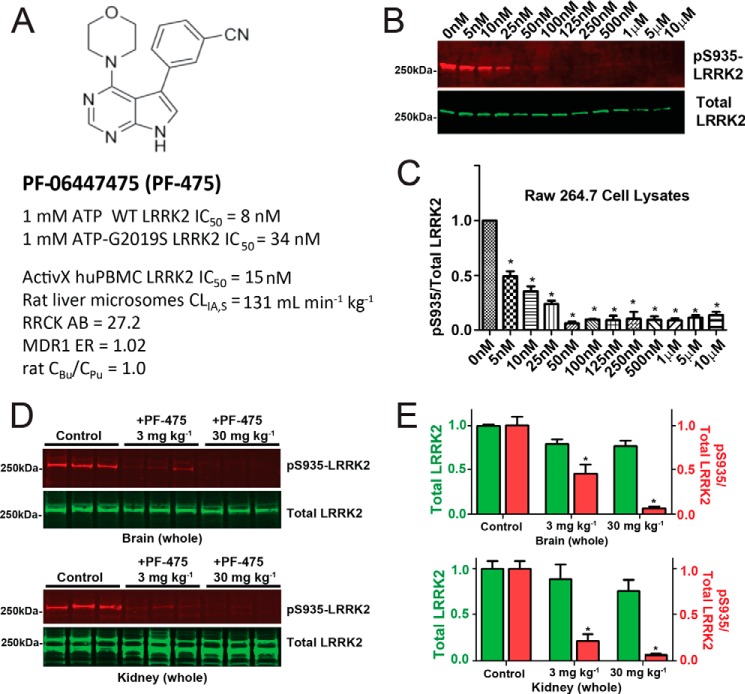
FIGURE 2.
Efficacy and pharmacodynamic properties of the LRRK2 kinase inhibitor PF-06447475. A, the structure of PF-06447475. LRRK2 kinase inhibitory activity was measured using recombinant full-length, GST-tagged LRRK2 protein and LRRKtide as a surrogate kinase substrate in a FRET assay in the presence of 1 mm ATP. The inhibitory potential was also calculated with a commercial ActivX assay in human peripheral blood monocytic cells (PBMCs). Rat liver microsome stability, passive permeability (RRCK cells), and P-gp efflux ratios (MDR1 cells) are shown. Brain availability is indicated by equivalency in rat unbound brain concentrations (CBu) to unbound plasma concentrations (CPu). B, cells from the mouse macrophage cell line raw 264.7 were treated with the indicated concentration of PF-06447475 for a period of 24 h before protein lysate generation and analysis for Ser(P)-935 and total LRRK2 expression by Western blot. C, a half-maximal inhibitor concentration was observed at ∼5 nm with respect to the ratio of Ser(P)-935 to total LRRK2 levels. D, groups of six (three male and three female) Sprague-Dawley rats were treated with PF-06447475 or vehicle control (p.o. b.i.d.) for 14 days and sacrificed 90 min after the last dose. Whole brains and kidneys were removed rapidly and processed to protein lysates to quantify Ser(P)-935-LRRK2 and total LRRK2. Signals from 50 μg of total protein, as determined by BCA assay, were analyzed per lane. E, quantification of the LRRK2 signal and the ratio of Ser(P)-935 to total LRRK2 in both brain and kidney. *, p < 0.01, calculated by one-way analysis of variance with Tukey's post-hoc test (C and E). All other group comparisons were not significant (p > 0.05) compared with control groups (Tukey's post hoc test). Data are means ± S.E.