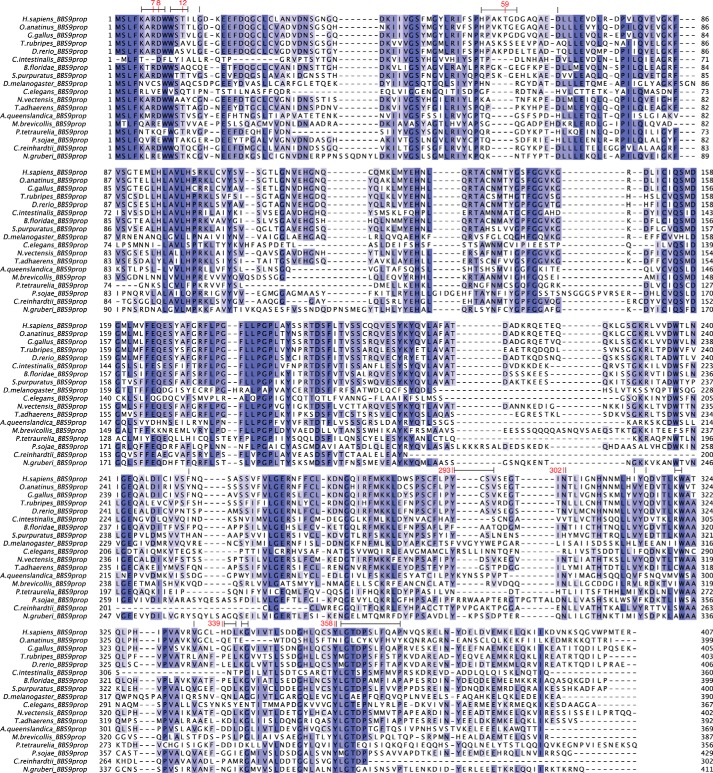
FIGURE 8.
MSA of the BBS9 N-terminal domain from 18 BBS9-containing eukaryotes. Residues are colored according to sequence identity, from white to blue. Numbered above the MSA, in red, are residues that participate in sequence-specific interactions within the HsBBS9 homodimer interface (hydrogen bonds and salt bridges). Residue ranges marked by black lines above the MSA denote amino acids buried by the interface (van der Waals interactions). Species were chosen for inclusion in the MSA based on Bork and co-workers and Dawson and co-workers (44, 45), to obtain a diverse sampling of eukaryotes and are ordered according to increasing distance from Homo sapiens. BBS9 is notably absent from land plants and fungi. The alignment comprises 13 metazoa (7 Chordata, 1 Arthropoda, 1 Nematoda, 1 Echinodermata, 1 Placozoa, 1 Cnidaria, and 1 Porifera), 1 Excavata, 1 protist (choanoflagellate), 1 plantae (green algae/Chlorophyta), and 2 protozoa (Chromalveolata).