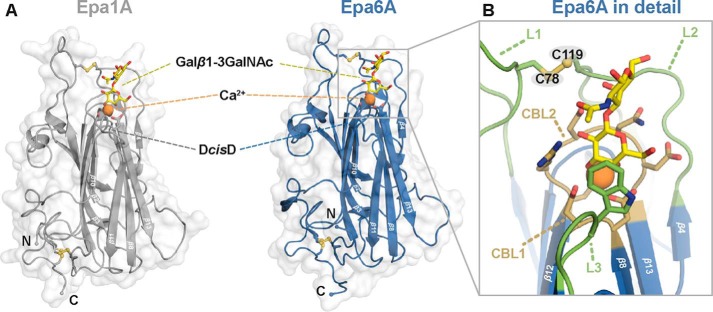
FIGURE 6.
Overall structural features of Epa6A and Epa1A. A, overall fold of Epa6A (blue) shows a β-sandwich comparable with that of Epa1A (gray). The complex structures of Epa6A and Epa1A show a bound T-antigen ligand (Galβ1–3GalNAc, yellow) complexed by a calcium ion (orange) via a DcisD motif that is highly conserved in fungal adhesins. B, selectivity and affinity in ligand binding is achieved by two calcium binding loops (CBL1 and CBL2; brown) in combination with three flexible loops, L1 to L3 (green). L1 and L2 are connected by a disulfide bridge via Cys-78 and Cys-119, which shields the binding pocket from surrounding solvent. L3 contains a tryptophan residue (green) that is highly conserved in Epa adhesins and is essential for ligand binding.