Figure 4.
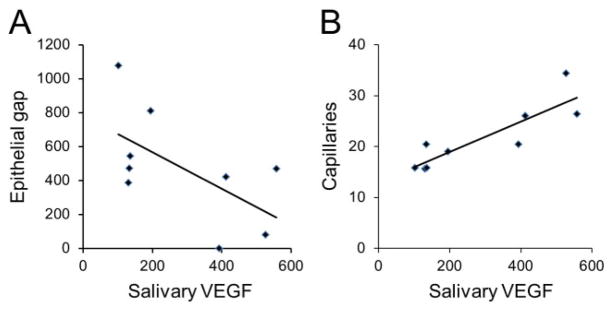
Salivary VEGF level is inversely correlated to epithelial gap and positively correlated to neovascularization. Pear-son’s correlation coefficient was used to correlate salivary VEGF levels to epithelial gap and neovascularization. Same group of mice (from sham and SMG sialoadenectomy groups) are used in the analysis in both A and B. At day 3 postpalatal mucosal wounding, salivary VEGF levels are inversely correlated to epithelial gap or impaired wound healing (A, Pearson’s correlation coefficient = −0.6, p < 0.05) and positively correlated to the number of vessels per HPF (B, Pearson’s correlation coefficient = 0.87, p < 0.01). HPF, high-power field; SMG, submandibular gland; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.
