Figure 1.
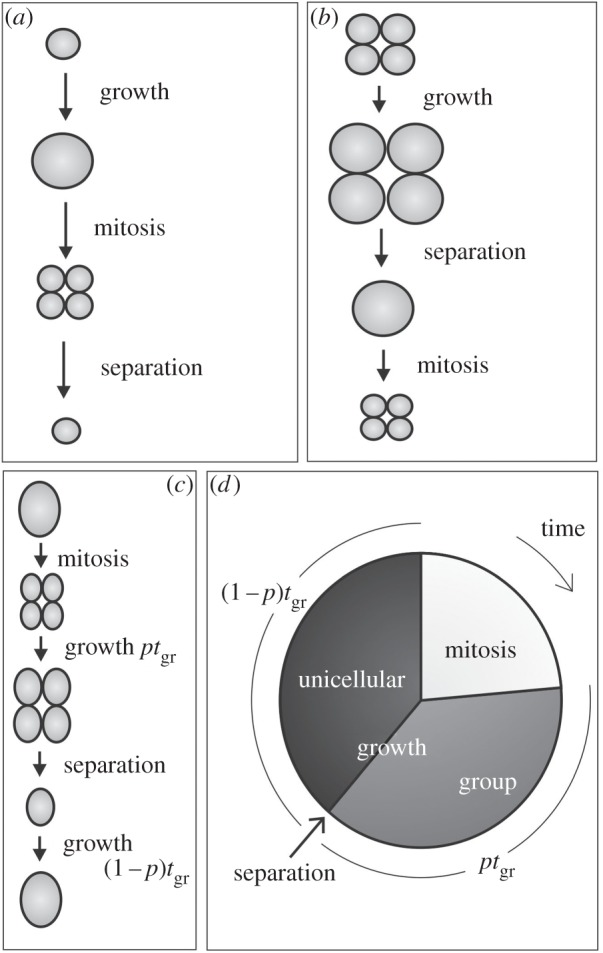
Life cycles. (a) Unicellular life cycle, as seen in species like Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. (b) Group life cycle, as seen in species like Tetrabaena socialis [11]. (c) A cell first grows as a part of a group for a given amount of time ptgr before leaving the group and continuing its life as a unicell. (d) As the life cycle variable p changes from 0 to 1, the order of cell cycle events changes and the separation stage occurs after cell growth in the group life cycle instead of before growth in the unicellular cycle.
