Figure 1.
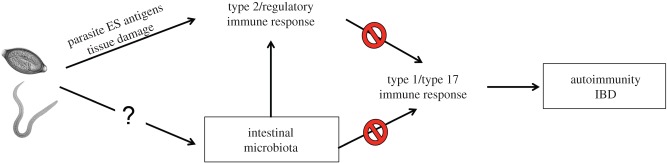
Potential role for microbiota in helminth-mediated suppression of autoimmune diseases? Helminths, including Trichuris sp. and hookworms are thought to limit the severity of IBDs and autoimmune diseases via promotion of type 2 and regulatory T cell responses that counteract pro-inflammatory type 1 or type 17 immune responses. However, emerging evidence suggests that helminth-mediated immune modulation may be, in part, due to alterations in the composition of the intestinal microbiota, which can profoundly influence immune cell development and function in the intestine. ES, excretory/secretory. (Online version in colour.)
