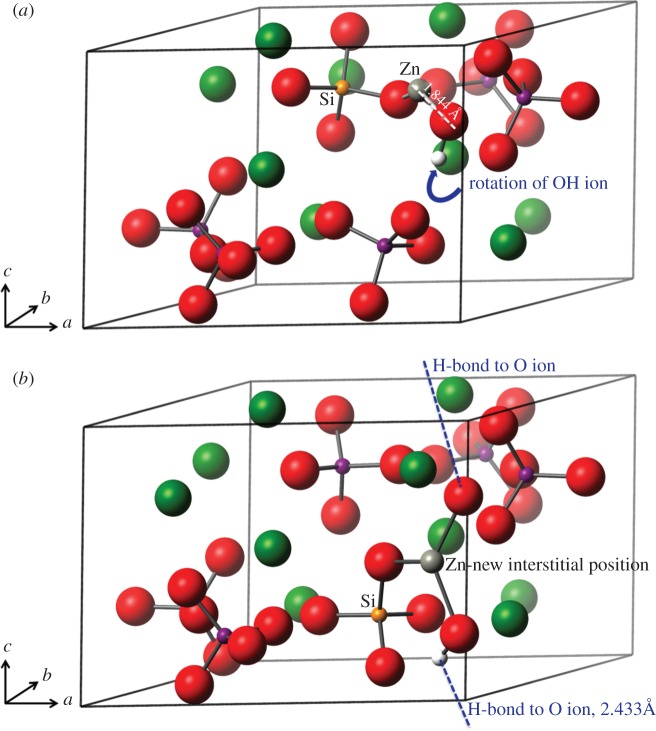
Figure 5.
(a) Silicate substitution and a zinc ion replacing a calcium ion. One hydroxyl ion has been removed from the c-axis for charge compensation. The zinc ion is bonded to the hydroxyl ion oxygen atom and one of the silicate ion oxygen atoms. The hydroxyl ion has been pulled off the c-axis. (b) Silicate substitution with a charge compensatory H atom positioned on the silicate ion. The zinc substitution is on the c-axis between two oxygen ions. The hydrogen atom has reattached to one of the c-axis oxygen atoms and the zinc is strongly bonded to both the c-axis oxygen atoms. Oxygen is shown in red, calcium green, phosphorus purple, zinc grey, silicon orange and hydrogen in white. (Online version in colour.)