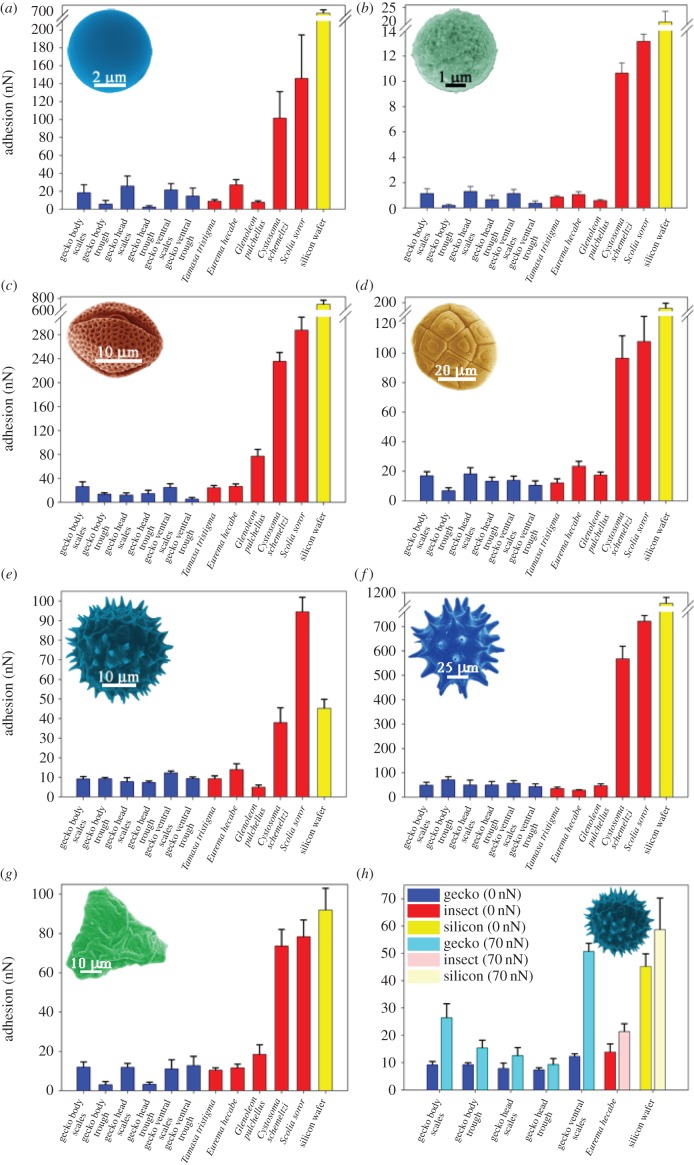
Figure 6.
Adhesion measurement values (in nN), using AFM probes of various pollen and spheres, interacting with the gecko dorsal (body), head and ventral skin regions at locations on the scales and areas between the scales (troughs). For comparison, other surfaces are also illustrated including insect wing membranes which have previously demonstrated ultra-low adhesion and high adhesion. The topography and measured static contact angles for the insect surfaces are shown in electronic supplementary material, figure S3. (a) Interactions of silica particles, (b) C18 partciles, (c) E. leucocephala Snowflake bush, (d) A. aneura wattle, (e) T. procumbens daisy, (f) H. rosa-sinensis, (g) Grevillea longistyla × G. venusta grevillea Firesprite cultivar; (h) the comparative adhesion at two distinct force loadings of T. procumbens on the gecko and other surfaces. Note that (a–d,f) contain axis breaks as a result of the very high adhesional values between the particle/pollen and Silicon wafer. Error bars—standard error values. (Online version in colour.)