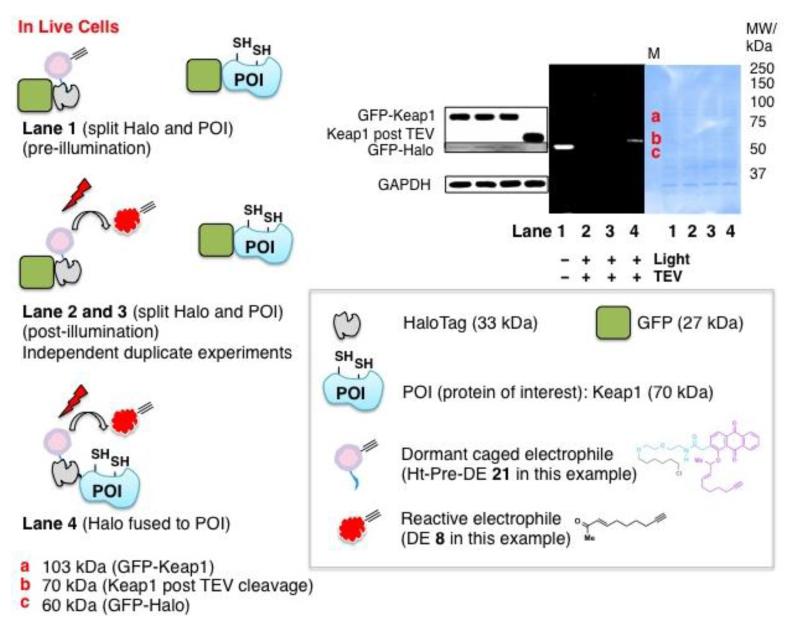
Figure 7.
The mechanistic basis of T-REX platform supports proximity-induced reactivity concept within the “target–signal encounter complex”. In-cell T-REX experiment in which Halo and Keap1 were not fused failed to deliver electrophile DE 8 to Keap1 using Ht-Pre-DE 21 and subsequent illumination (Lane 2 and 3, independent duplicates). By contrast, successful targeted delivery was achieved when Halo and Keap1 were fused (Lane 4 and also see Figre S2b). Schematic representations for each Lane are shown on the left. DE adduction of Keap1 (post TEV-protease cleavage) was observed (band b on gel) as expected in Lane 4. Western blot data and coomassie-stained PVDF were also shown. Bands a, b, and c correspond to GFP-Keap1 (103 kDa), Keap1 (70 kDa, post TEV-cleavage), and GFP-Halo (60 kDa), respectively. “M” indicates the ladder lane. Inset shows reference to the schematics. Rabbit polyclonal anti-GFP primary antibody (sc-8334) was used to probe GFP-Halo protein. All forms of proteins containing Keap1 were probed by mouse monoclonal anti-Keap1 primary antibody (Ab119403). See also Figure S3 and S4 for analogous data sets with non-GFP-fulsed Keap1.