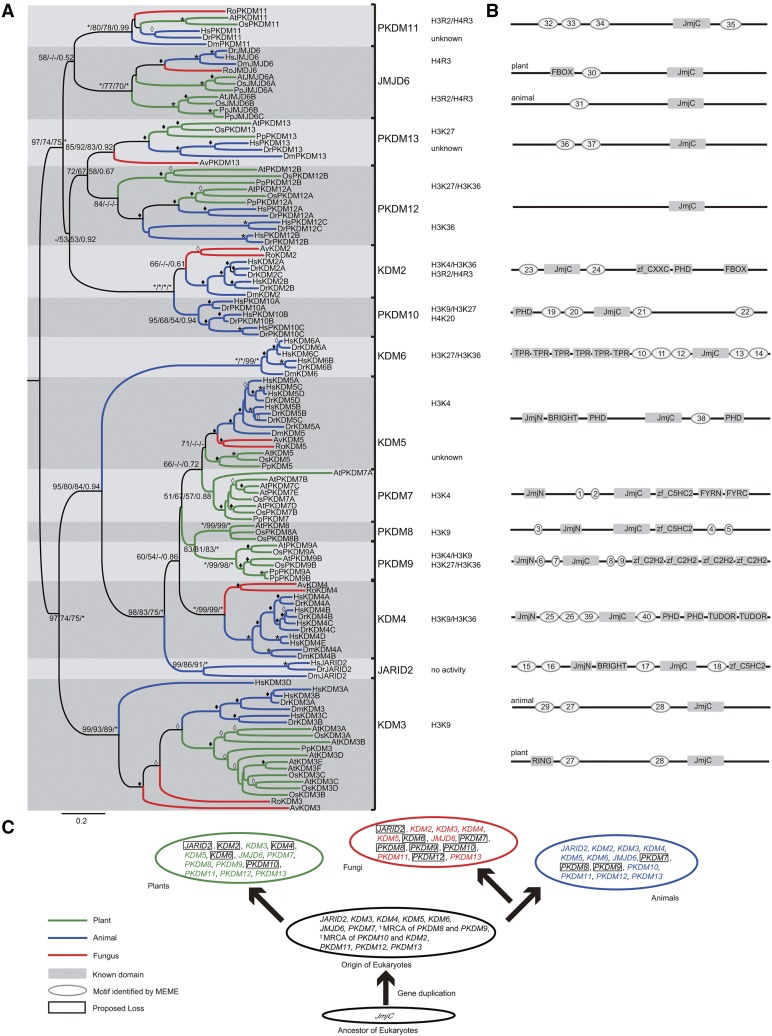
Figure 2.
Phylogeny of representative JmjC genes from plants, animals, and fungi. A, Evolutionary relationship between JmjC genes from eight representative species (Chordata: Hs, Homo sapiens; Dr, Danio rerio. Arthropoda: Dm, Drosophila melanogaster. Basidiomycota: Av, A. bisporus var bisporus. Zygomycota: Ro, Rhizopus oryzae. Angiosperms: At, Arabidopsis; Os, rice. Bryophyta: Pp, Physcomitrella patens). Tree topology constructed using MEGA is shown here. For major nodes, NJ and ML (ML bootstrap [BS] values were generated by PhyML (version 3.0) and RAxML (version 7.0), respectively), BS values above 50%, followed by Bayesian posterior probability (PP) values are shown. For minor nodes, empty diamonds represent BS values of 50% to 69% and solid diamonds mark BS values of 70% to 99% from NJ analysis. For major and minor nodes, asterisks indicate BS/PP values of 100%/1. Substrate specificities for residues of histone tails are indicated for all subfamilies with demonstrated demethylase activity. B, Highly conserved non-JmjC amino acid motifs in each JmjC subfamily. An idealized representation of a typical member of each JmjC subfamily is shown, with known domains drawn as shaded rectangles and other conserved motifs drawn as shaded ovals. The diagrams are not drawn to scale. The sequences of each motif in gene family members are given in Supplemental Table S3. C, Model of the evolutionary history of the JmjC gene family. In different kingdoms, the JmjC gene experienced several specific duplication events associated with the species divergence.