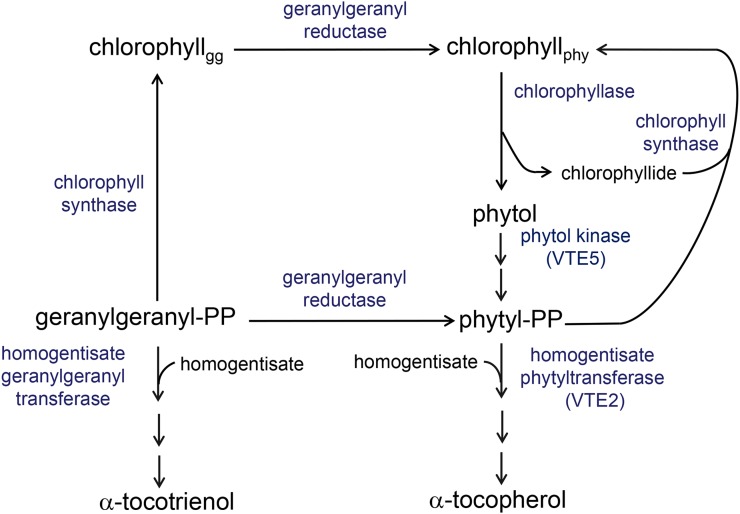
Figure 1.
Pathways for de novo PDP synthesis and tocopherol biosynthesis in photosynthetic organisms. Tocopherol biosynthesis is initiated by the prenylation of homogentisate with PDP catalyzed by HPT. PDP is synthesized by the reduction of geranylgeranyl either in the diphosphate form or as the hydrophobic sidechain of chlorophyll by the activity of GGR, and recent evidence has pointed to that at least 80% of PDP synthesis proceeds through the reduction of geranylgeranyl bound to chlorophyll in Arabidopsis (Ischebeck et al., 2006; Valentin et al., 2006). This pathway for PDP synthesis requires an array of enzymes in addition to GGR, including chlorophyll synthase to esterify geranylgeranyl to chlorophyll, chlorophyllase to release phytol from chlorophyll, and two phytol kinases, including VTE5, to convert released phytol to PDP. The esterification of chlorophyllide with GGDP catalyzed by chlorophyll synthase is the primary reaction for chlorophyll biosynthesis, and esterification of chlorophyllide with PDP is a secondary reaction for chlorophyll synthesis catalyzed by chlorophyll synthase using PDP derived from chlorophyll degradation. An alternative fate for GGDP is condensation with homogentisate for biosynthesis of the tocotrienol form of vitamin E (Cahoon et al., 2003; Yang et al., 2011). chlorophyllgg, Chlorophyll linked to a geranylgeranyl moiety; chlorophyllphy, chlorophyll linked to a phytyl moiety.