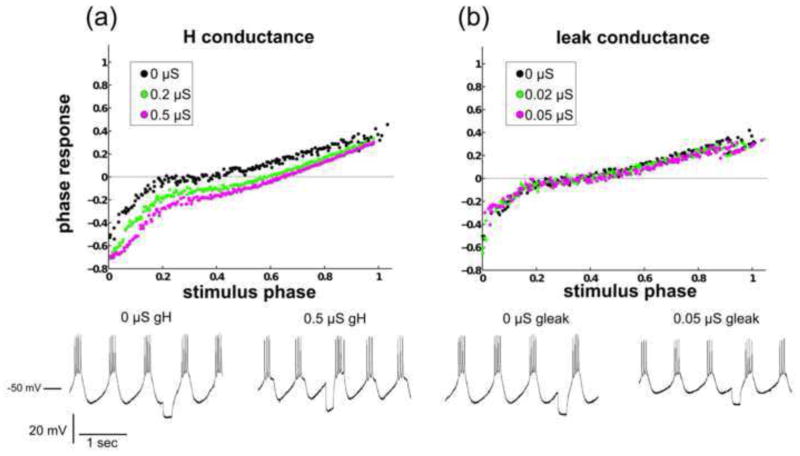
Fig. 10. Dynamic-clamp-injected H current advances and regularizes the PRC.
(a) As the H conductance is increased, the PRC is advanced and its variability is reduced. Voltage traces are shown for the lowest and highest levels of dynamic-clamp injected H current. In this example, ḡH was a significant factor in altering the PRC (p < 10−12). (b) Here, ḡleak was a significant factor in altering the PRC (p = 0.0003). However, the change in the phase response at any given stimulus phase as ḡleak is increased is relatively small. Voltage traces are shown for the lowest and highest levels of dynamic-clamp-injected leak current