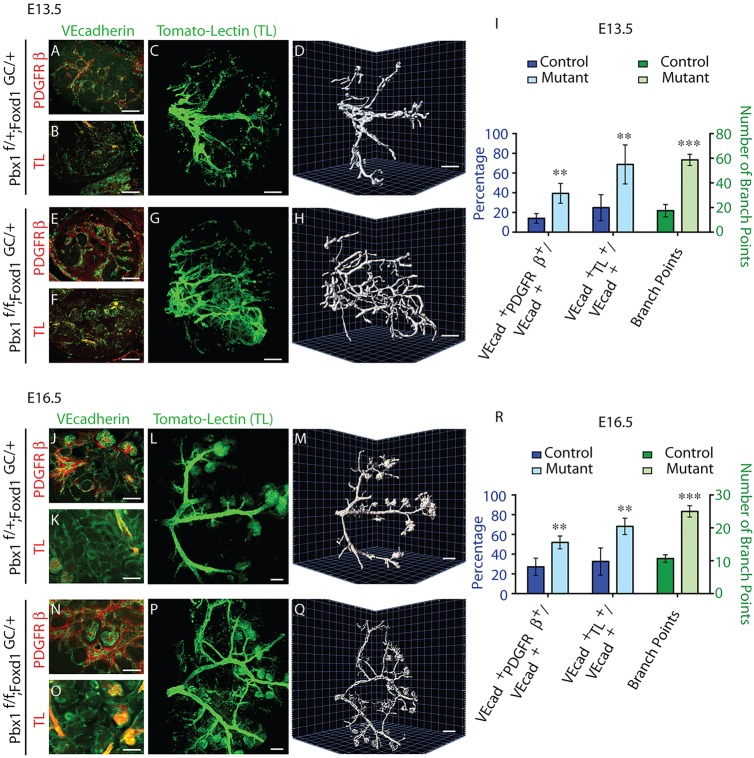
Fig. 4.
Pbx1 in the Foxd1-VMC lineage is essential for arterial patterning. (A-H,J-Q) E13.5 (A-H) and E16.5 (J-Q) control Pbx1f/+;Foxd1GC/+ (A-D,J-M) and mutant Pbx1f/f;Foxd1GC/+ (E-H,N-Q) kidneys processed by IF (A,B,E,F,J,K,N,O) for the detection of PDGFRβ (A,E,J,N) and VE-Cadherin (A,B,E,F,J,K,N,O). Intravital labeling with TL was used to label blood-conducting vessels. IF analyses of kidney sections subsequent to intravital dye labeling (B,F,K,O). To determine the gross architecture of the renal arterial tree, intravital dye labeling was performed with TL, and blood-conducting vessels were subsequently analyzed in three dimensions in intact kidneys. C,G,L,P are planar images; D,H,M,Q show 3D rendering. n>3 per genotype. Scale bars: 50 µm. (I,R) Quantification of the area of the VECAD+ vascular network associated with PDGFRβ+ cells (PDGFRβ+/VECAD+); area of the VECAD+ vascular network that conducts blood (TL+/VECAD+); and arterial branch points (mean±s.d.); n>3 per genotype; **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.