Figure 1.
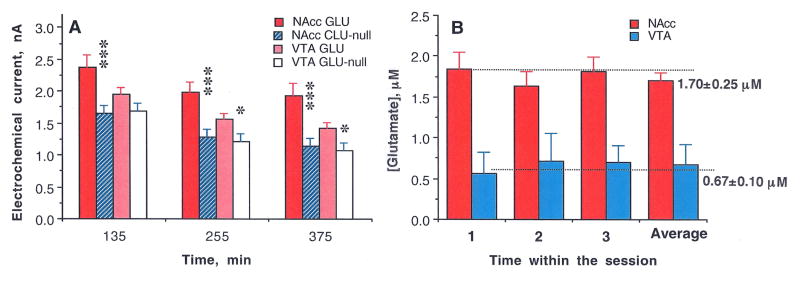
(A) Mean (±SEM) values of basal electrochemical currents recorded by GLU and GLU-null sensors in the NAcc and VTA at three time points (from the moment of sensor insertion in the brain) before each consecutive nicotine injection. In each case, the mean value for GLU sensors was larger than the corresponding value for GLU-null sensors (*, p<0.05; ** and ***, p<0.001; Student’s t-test) and the current values detected by GLU sensors in the VTA were consistently lower than those in the NAcc. By subtracting these values and converting them to concentrations (B) we found that basal levels of GLU in the NAcc are significantly larger than those in the VTA. Importantly, despite the decreases in absolute values of currents detected during the course of the experiment, the difference between GLU and GLU-null sensors that reflects [GLU] remained relatively stable during the entire experiment.
