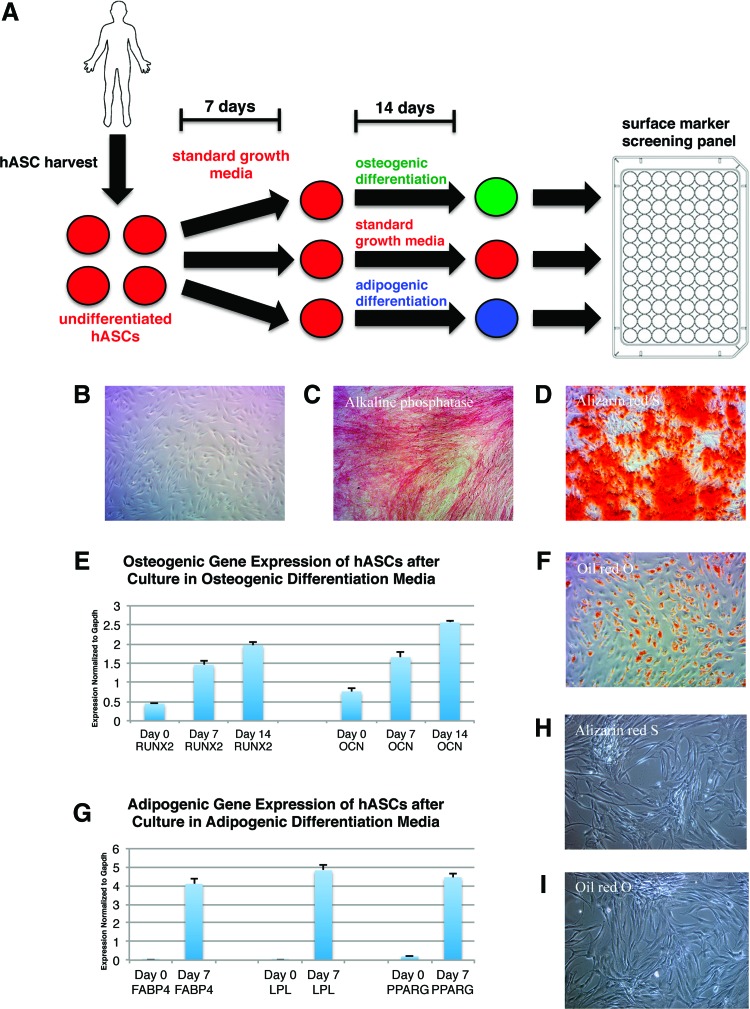
FIG. 1.
Osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stromal cells (hASCs). (A) Schematic showing experimental overview for the identification of surface markers differentially regulated after osteogenic or adipogenic differentiation. (B) Light microscope image of undifferentiated hASCs from a single donor after 21 days in culture. (C) Alkaline phosphatase staining in hASCs harvested from a single donor on day 7 of osteogenic differentiation. (D) Alizarin red S staining in hASCs harvested from a single donor on day 14 of osteogenic differentiation. (E) Quantitative real-time–polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) of RUNX2 and Osteocalcin (OCN) expression in hASCs harvested from a single donor on day 7 and 14 of osteogenic differentiation. Errors bars represent one standard deviation with an n=3 wells. (F) Oil red O staining in hASCs harvested from a single donor on day 7 of adipogenic differentiation. (G) qRT-PCR of FABP4, LPL, and PPARG expression in hASCs harvested from a single donor on day 7 of adipogenic differentiation. Errors bars represent one standard deviation with an n=3 wells. (H) Alizarin red S staining on hASCs maintained in vitro in plain medium (no differentiation components added) for 21 days from a single donor. (I) Oil red O staining on hASCs maintained in vitro in plain medium (no differentiation components added) for 21 days from a single donor. Color images available online at www.liebertpub.com/tea