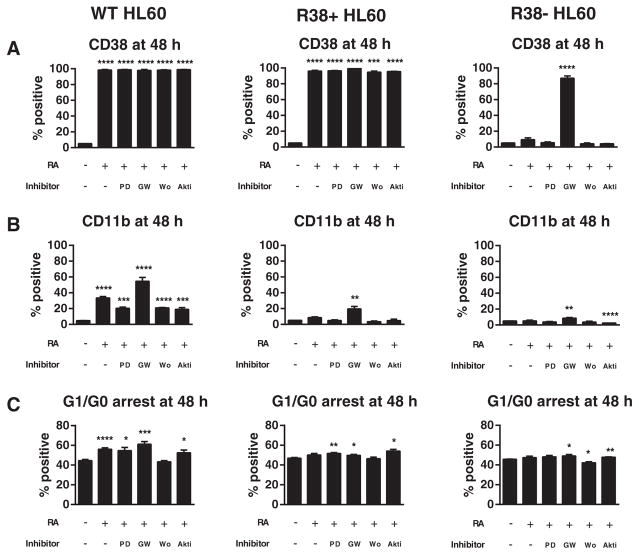
Fig. 1.
Phenotypic markers during RA and kinase inhibitor co-treatment in HL-60. Wild-type (WT), R38+ and R38−HL-60 cells were treated for 48 h with 1 μM RA, or RA combined with 2 μM PD98059 (PD), 2 μM GW5074 (GW), 1 μM wortmannin (Wo), or 1 μM Akti-1/2 (Akti) and analyzed by flow cytometry for (A) CD38 expression, (B) CD11b expression, or (C) G1/G0 cell cycle arrest. Error bars represent standard error. Asterisks for p-values of treatment group means compared to control indicate whether p < 0.0001 (****), p < 0.001 (***), p < 0.01 (**) or p < 0.05 (*). (A) CD38 is maximally expressed in WT and R38+ HL-60 and not inhibited by any kinase inhibitor treatment. GW5074 significantly increase CD38 expression in R38−cells. (B) CD11b is increased by RA and enhanced by GW5074 in WT HL-60 cells, while all other co-treatments reduced the RA-induced CD11b expression. GW5074 can significantly increase CD11b expression in R38+ and R38−. (C) GW5074 can enhance RA-induced G1/G0 arrest in WT HL-60 and rescue G1/G0 arrest in R38+ and R38−. Akti-1/2 and PD98059 also tended to increase G1/G0 arrest.