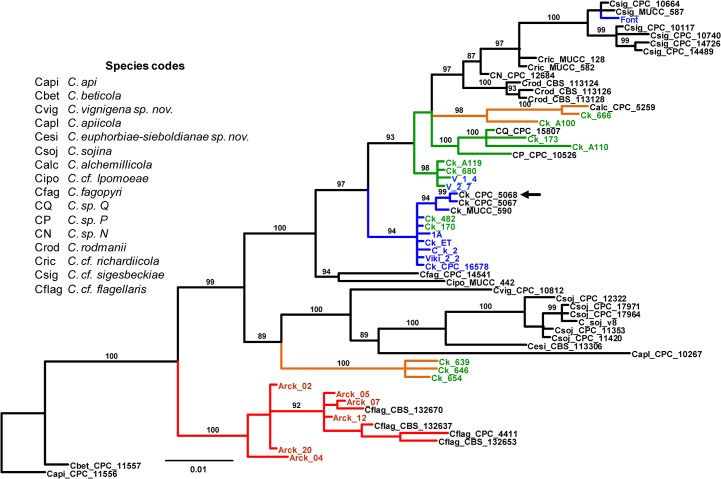
Fig 2. Bayesian phylogeny (consensus tree) showing the relationships among causal agents of Cercospora leaf blight and purple seed stain of soybean and other closely related species.
Fungal isolates were obtained from either purple-stained soybean seeds or infected leaves. The dataset was1566 bases long and resulted from the concatenation of five nuclear genes (act, cal, his, ITS, and tef). Branch lengths are drawn to scale; nodal support values are given as posterior probabilities (%) above the branches (when > 85%). Scale bar corresponds to the expected number of substitutions per site. Color in terminals according to the origin of the isolates: blue, Argentina; green, Brazil; red, United States; and black, data from 6]. Color in branches according to lineage: blue, lineage 1; green, lineage 2; orange, lineage 3; and red, lineage 4. Black arrow indicates the ex-type strain of C. kikuchii (CPC_5068). Gene codes: act, actin; cal, calmodulin; his, histone H3; ITS, internal transcribed spacers and intervening 5.8S nrDNA; tef, translation elongation factor 1-alpha.