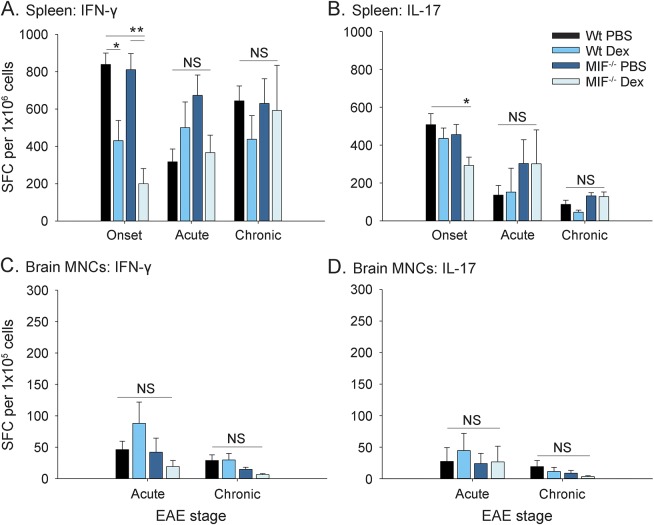
Figure 2. Effect of Dex on cytokine production by MIF−/− or Wt T cells in EAE.
Wild-type (Wt) and macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF)−/− mice were immunized to induce experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) and injected intraperitoneally with 10 mg/kg dexamethasone (Dex) vs phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) control for 3 continuous days upon onset of disease, as shown in figure 1B. Spleens (A, B) and brain mononuclear cells (MNCs) (C, D) of EAE mice were harvested at different time points and restimulated with MOG35-55 peptide. The frequencies of Th1 and Th17 cytokine-producing T cells were measured by ELISPOT assay as described in the Methods. Shown are pooled data from 2 to 4 independent experiments (mean ± SEM; onset, n = 7–14 mice per group from day 10 postimmunization and after 3 injections of Dex or PBS; acute, n = 5 mice per group from day 16–24 postimmunization when PBS groups reached peak score of 2 or higher; chronic, n = 6–8 mice per group from day 26–36, usually 10 days after PBS groups remitted from peak of disease; analysis of variance; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01). IFN = interferon; IL = interleukin; NS = not significant; SFC = spot-forming cells.