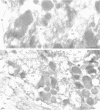
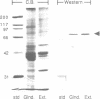
Abstract
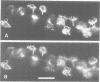
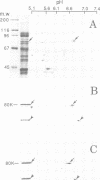
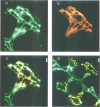
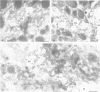
Stimulation of gastric acid secretion in parietal cells involves the translocation of the proton pump (H,K-ATPase) from cytoplasmic tubulovesicles to the apical membrane to form long, F-actin-containing, microvilli. Following secretion, the pump is endocytosed back into tubulovesicles. The parietal cell therefore offers a system for the study of regulated membrane recycling, with temporally separated endocytic and exocytic steps. During cAMP-mediated stimulation, an 80 kDa peripheral membrane protein becomes phosphorylated on serine residues. This protein is a major component, together with actin and the pump, of the isolated apical membrane from stimulated cells, but not the resting tubulovesicular membrane. Here we show that the gastric 80 kDa phosphoprotein is closely related or identical to ezrin, a protein whose phosphorylation on serine and tyrosine residues was recently implicated in the induction by growth factors of cell surface structures on cultured cells [Bretscher, A. (1989) J. Cell Biol., 108, 921-930]. Light and electron microscopy reveal that ezrin is associated with the actin filaments of the microvilli of stimulated cells, but not with the filaments in the terminal web. In addition, a significant amount of ezrin is present in the basolateral membrane infoldings of both resting and stimulated cells. Extraction studies show that ezrin is a cytoskeletal protein in unstimulated and stimulated cells, and its association with the cytoskeleton is more stable in stimulated cells. These studies indicate that ezrin is a membrane cytoskeletal linker that may play a key role in the control of the assembly of secretory apical microvilli in parietal cells and ultimately in the regulation of acid secretion. Taken together with the earlier studies, we suggest that ezrin might be a general substrate for kinases involved in the regulation of actin-containing cell surface structures.
Full text
PDF
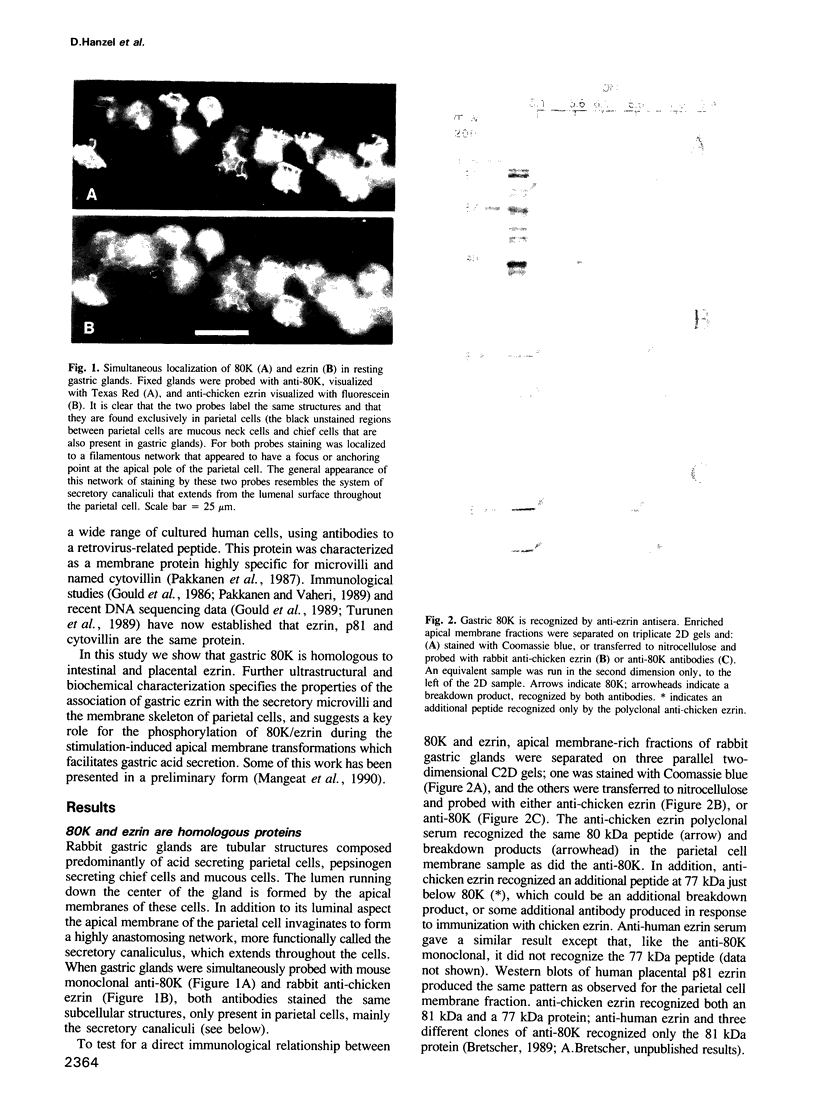
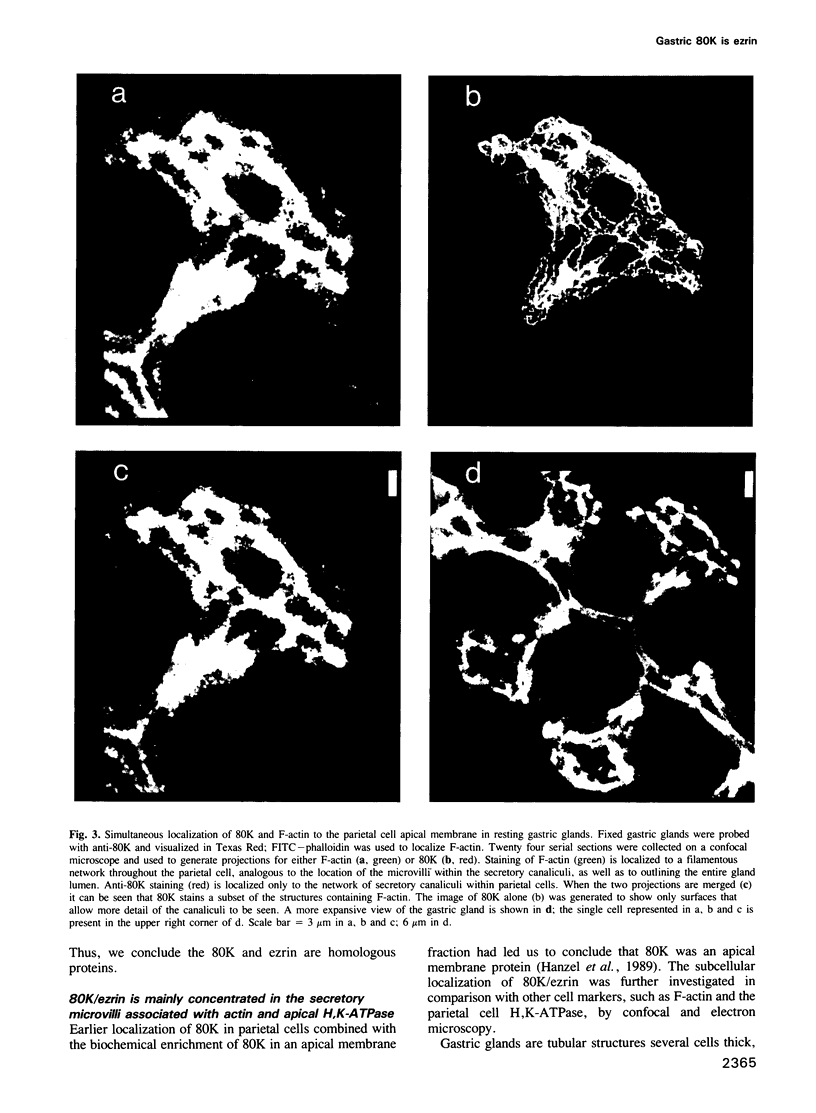



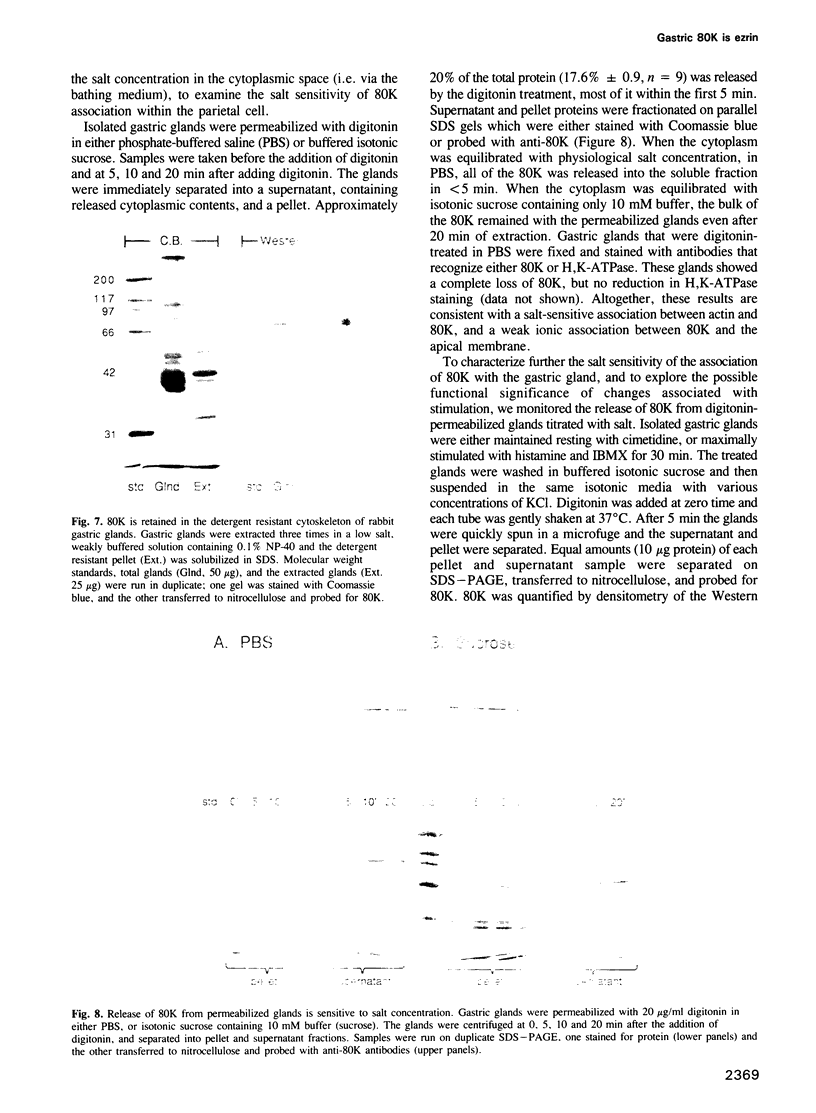
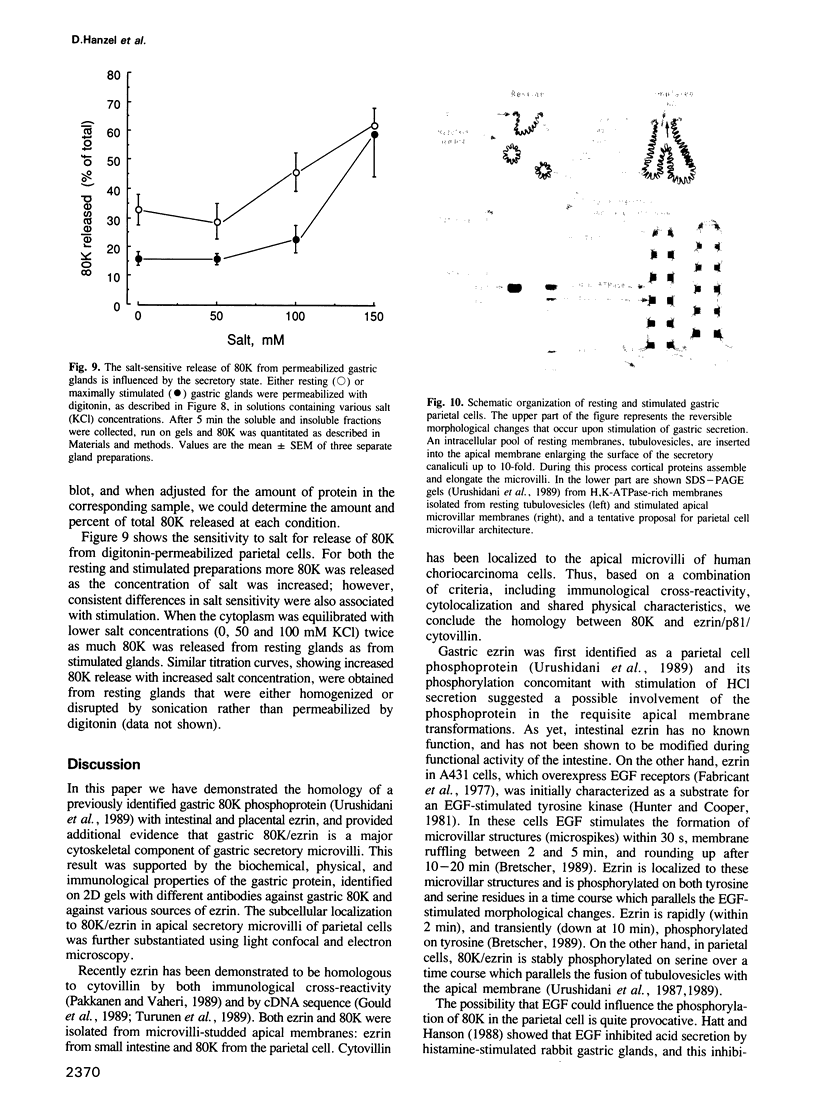



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berglindh T., Obrink K. J. A method for preparing isolated glands from the rabbit gastric mucosa. Acta Physiol Scand. 1976 Feb;96(2):150–159. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1976.tb10184.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black J. A., Forte T. M., Forte J. G. The effects of microfilament disrupting agents on HCl secretion and ultrastructure of piglet gastric oxyntic cells. Gastroenterology. 1982 Sep;83(3):595–604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher A. Rapid phosphorylation and reorganization of ezrin and spectrin accompany morphological changes induced in A-431 cells by epidermal growth factor. J Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;108(3):921–930. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.3.921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duerr A., Pallas D., Solomon F. Molecular analysis of cytoplasmic microtubules in situ: identification of both widespread and specific proteins. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):203–211. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90516-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabricant R. N., De Larco J. E., Todaro G. J. Nerve growth factor receptors on human melanoma cells in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):565–569. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forte J. G., Black J. A., Forte T. M., Machen T. E., Wolosin J. M. Ultrastructural changes related to functional activity in gastric oxyntic cells. Am J Physiol. 1981 Nov;241(5):G349–G358. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1981.241.5.G349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forte J. G., Hanzel D. K., Urushidani T., Wolosin J. M. Pumps and pathways for gastric HCl secretion. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1989;574:145–158. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1989.tb25153.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forte T. M., Machen T. E., Forte J. G. Ultrastructural changes in oxyntic cells associated with secretory function: a membrane-recycling hypothesis. Gastroenterology. 1977 Oct;73(4 Pt 2):941–955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould K. L., Bretscher A., Esch F. S., Hunter T. cDNA cloning and sequencing of the protein-tyrosine kinase substrate, ezrin, reveals homology to band 4.1. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):4133–4142. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08598.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould K. L., Cooper J. A., Bretscher A., Hunter T. The protein-tyrosine kinase substrate, p81, is homologous to a chicken microvillar core protein. J Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;102(2):660–669. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.2.660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanzel D. K., Urushidani T., Usinger W. R., Smolka A., Forte J. G. Immunological localization of an 80-kDa phosphoprotein to the apical membrane of gastric parietal cells. Am J Physiol. 1989 Jun;256(6 Pt 1):G1082–G1089. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1989.256.6.G1082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatt J. F., Hanson P. J. Inhibition of gastric acid secretion by epidermal growth factor. Effects on cyclic AMP and on prostaglandin production in rat isolated parietal cells. Biochem J. 1988 Nov 1;255(3):789–794. doi: 10.1042/bj2550789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helander H. F., Hirschowitz B. I. Quantitative ultrastructural studies on gastric parietal cells. Gastroenterology. 1972 Dec;63(6):951–961. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hersey S. J., Steiner L. Acid formation by permeable gastric glands: enhancement by prestimulation. Am J Physiol. 1985 May;248(5 Pt 1):G561–G568. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1985.248.5.G561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangeat P. H. Interaction of biological membranes with the cytoskeletal framework of living cells. Biol Cell. 1988;64(3):261–281. doi: 10.1016/0248-4900(88)90001-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean I. W., Nakane P. K. Periodate-lysine-paraformaldehyde fixative. A new fixation for immunoelectron microscopy. J Histochem Cytochem. 1974 Dec;22(12):1077–1083. doi: 10.1177/22.12.1077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercier F., Reggio H., Devilliers G., Bataille D., Mangeat P. A marker of acid-secreting membrane movement in rat gastric parietal cells. Biol Cell. 1989;65(1):7–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercier F., Reggio H., Devilliers G., Bataille D., Mangeat P. Membrane-cytoskeleton dynamics in rat parietal cells: mobilization of actin and spectrin upon stimulation of gastric acid secretion. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):441–453. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pakkanen R., Hedman K., Turunen O., Wahlström T., Vaheri A. Microvillus-specific Mr 75,000 plasma membrane protein of human choriocarcinoma cells. J Histochem Cytochem. 1987 Aug;35(8):809–816. doi: 10.1177/35.8.3298422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pakkanen R., Vaheri A. Cytovillin and other microvillar proteins of human choriocarcinoma cells. J Cell Biochem. 1989 Sep;41(1):1–12. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240410102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees D. J., Ades S. E., Singer S. J., Hynes R. O. Sequence and domain structure of talin. Nature. 1990 Oct 18;347(6294):685–689. doi: 10.1038/347685a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turunen O., Winqvist R., Pakkanen R., Grzeschik K. H., Wahlström T., Vaheri A. Cytovillin, a microvillar Mr 75,000 protein. cDNA sequence, prokaryotic expression, and chromosomal localization. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 5;264(28):16727–16732. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urushidani T., Hanzel D. K., Forte J. G. Characterization of an 80-kDa phosphoprotein involved in parietal cell stimulation. Am J Physiol. 1989 Jun;256(6 Pt 1):G1070–G1081. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1989.256.6.G1070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urushidani T., Hanzel D. K., Forte J. G. Protein phosphorylation associated with stimulation of rabbit gastric glands. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Sep 14;930(2):209–219. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(87)90033-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]