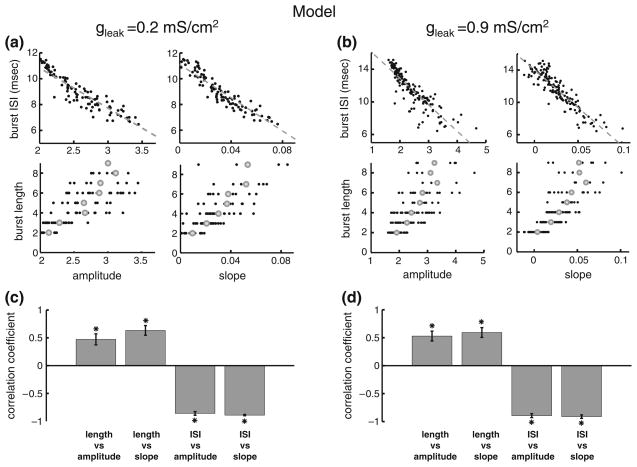
Fig. 4.
Effects of the membrane resistance on correlations between burst and stimulus attributes. (a): plots of burst attributes versus stimulus attributes for low leak conductance. The plots are: burst ISI vs. amplitude, upper left; burst ISI vs. slope, upper right; burst length vs. amplitude, lower left; burst length vs. slope, lower right. (b): plots of bursts attributes versus stimulus attributes for high leak conductance. The plots are: burst ISI vs. amplitude, upper left; burst ISI vs. slope, upper right; burst length vs. amplitude, lower left; burst length vs. slope, lower right. (c): ensemble averages over 10 stimulus presentations without noise of the correlation coefficients for each of the plots in panel A. (d): ensemble averages over 10 presentations of the stimulus presentations with a different realization of the noise of the correlation coefficients for each of the plots in panel B. “*” indicates statistical significance at the P=0.01 level using a signrank test