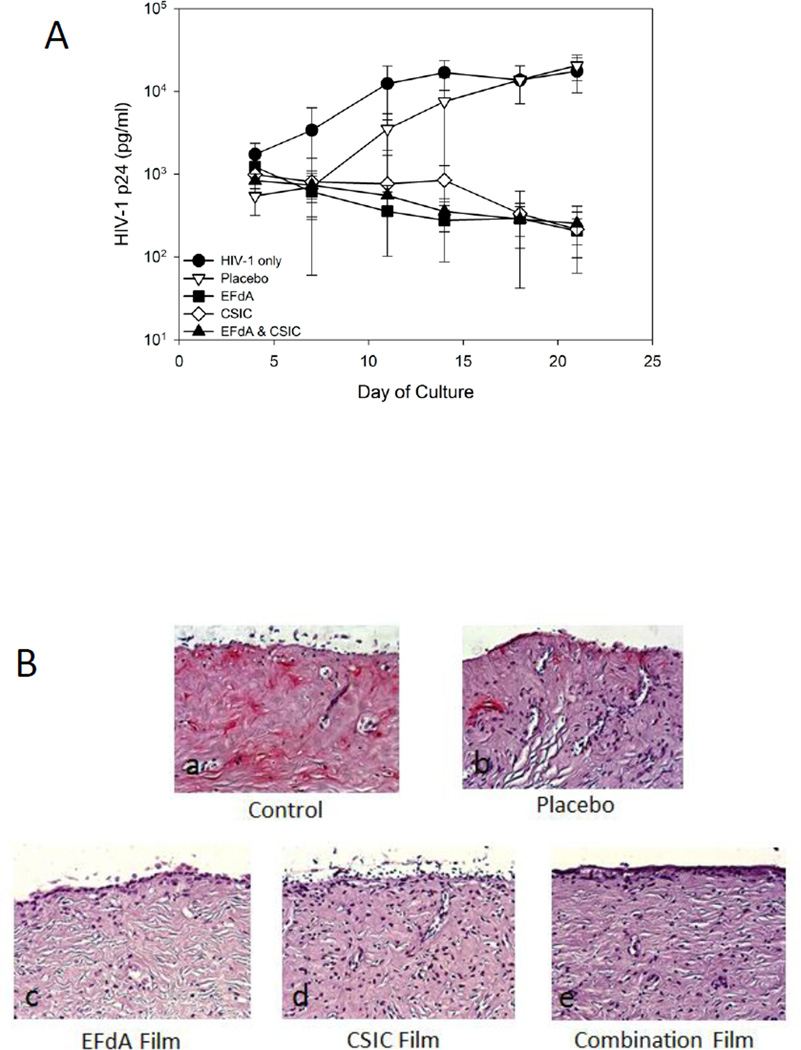
Fig.8.
Ex vivo efficacy of drug-loaded vaginal films using human ectocervical tissue explant cultures. (A) HIV-1 inhibition by drug-containing film formulations. Placebo film did not prevent HIV-1 infection of the ectocervical tissue. (B) Endpoint IHC staining of tissues treated with HIV-1 only (control), placebo film, EFdA film, CSIC film, and combination film. Tissues were exposed to the different film formulations overnight, followed by washing and 21 days of culture. At study end, the tissues were fixed and stained with p24 monoclonal antibody. The red color in the untreated control and placebo-treated tissues indicate p24-positive cells, reflecting the presence of HIV-infected cells. No HIV-infected cells were found in the drug-loaded film formulation-treated tissue samples. The IHC data are representative of 3 independent tissues.