Fig. 1.
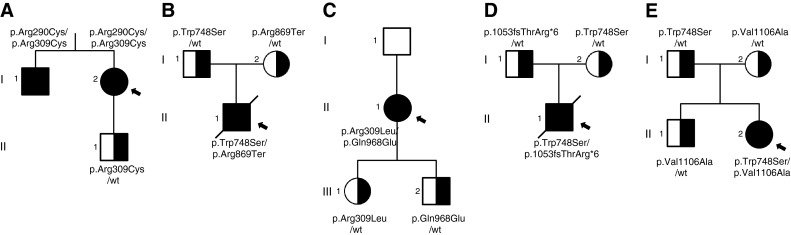
POLG variant distribution analysis in patients and their families. a Proband (I2) and her brother (I1) are both affected and have one known, but poorly characterised and one novel variant (p.Arg290Cys/p.Arg309Cys), whereas the proband’s healthy son (II1) is a carrier of the p.Arg309Cys variant. b Proband (II1) died at the age of 2.5 years due to liver failure caused by valproic acid administration. He carried heterozygous p.Trp748Ser mutation and heterozygous novel variant p.Arg869Ter. His parents (I1 and I2) are heterozygous carriers of either pathogenic mutation p.Trp748Ser (I1), or the novel variant p.Arg869Ter (I2). c Proband (II1) carries heterozygous pathogenic mutation p.Arg309Leu and heterozygous novel variant p.Gln968Glu. Her children (III1 and III2) are unaffected heterozygous carriers of pathogenic mutation p.Arg309Leu (III1), and the novel variant p.Gln968Glu (III2). The presence of p.Gln968Glu in the proband’s father (I1) was excluded, but due to the lack of biological material we were unable to perform the analysis for the presence of the p.Arg309Leu mutation. d The proband (II1) died at the age of 3.5 years after liver failure due to valproic acid administration. Both parents (I1 and I2) have either the novel p.Thr1053Argfs*6 (I1) variant or the known pathogenic mutation p.Trp748Ser (I2). e Proband (II2) carries heterozygous pathogenic mutation p.Trp748Ser together with heterozygous novel variant p.Val1106Ala. Her father (I1) is a carrier of the known pathogenic mutation p.Trp748Ser, whereas both her mother (I2) and brother (II1) have heterozygous novel variant p.Val1106Ala. All heterozygous family members are asymptomatic. Since the analysis of familial distribution of POLG variants present in families a–e indicates that all the probands are compound heterozygotes in trans, an autosomal recessive mode of inheritance is suggested
