Fig. 2.
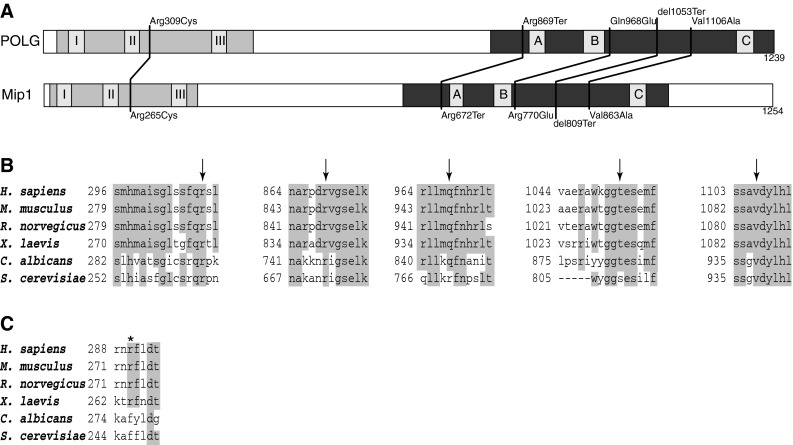
Modelling human POLG variants using the S. cerevisiae ortholog—Mip1p. a Schematic representation of POLG and Mip1 protein primary structure, with locations of the studied human POLG variants and the corresponding residues in S. cerevisiae Mip1p. The exonuclease domain is shown shaded light grey and the polymerase domain is shaded dark grey. Sequence of the linker region is not conserved. Blocks I, II, and III in the exonuclease domain, and A, B, and C in the polymerase domain are the regions of highest sequence conservation. b Alignment of the mitochondrial DNA polymerase amino acid sequences of selected vertebrate and yeast species in the regions of human variants selected for yeast modelling. Conserved residues (>0.5 consensus identity) are highlighted, arrows point to residues changed in the variant alleles under study. c Alignment of the mitochondrial DNA polymerase amino acid sequences of selected vertebrate and yeast species in the region around human Arg290 residue (marked with an asterisk), where lack of conservation between vertebrate and yeast sequences makes modelling of the Arg290Cys variant impractical
