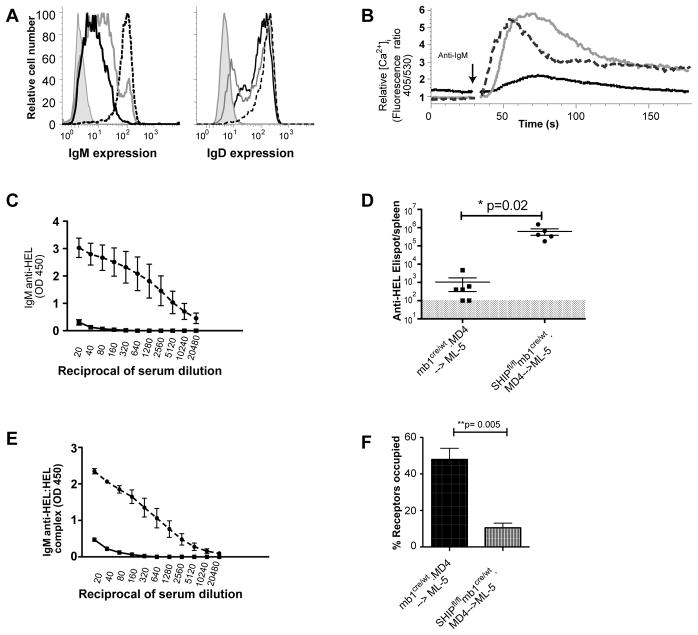
Figure 4. Lack of B cell anergy in SHIP-deficient MD4-->ML-5 bone marrow chimeric mice reflects ignorance.
Splenocytes and serum were isolated from chimeric ML-5 mice 12wk after transfer of MD4 bone marrow. A. IgM and IgD expression by SHIP-sufficient (black), SHIP-deficient (gray) B cells, as well as positive control MD4 B cells (dashed black) and negative control T cells (gray shaded). B. Cells were Indo1-AM loaded and B cell intracellular free calcium monitored before and after stimulation with 15 ng/mL HEL; responses of SHIP-1-sufficient (black), SHIP-1-deficient (gray) and MD4 SHIP-sufficient control B cells (dashed black) are shown. C. Serum IgM anti-HEL concentrations were determined by ELISA. Shown are antibody levels in mice containing SHIP-sufficient (square) and SHIP-deficient (circle) B cells. D. Splenic ASC were measured by ELISPOT. Shown are ASC in spleens of mice in which B cells were SHIP sufficient (squares) or SHIP deficient (circles). Shaded area reflects the 100 ASC/spleen limit of detection of the assay. E. IgMa anti-HEL:HEL immune complexes were measured by ELISA in serum from chimeric mice in which B cells were SHIP sufficient (squares) or SHIP deficient (circles). F. HEL occupancy of BCR on ex vivo SHIP-sufficient (black) and SHIP-deficient (gray) B cells. Experiment was repeated twice with 3–5 mice per experimental group.