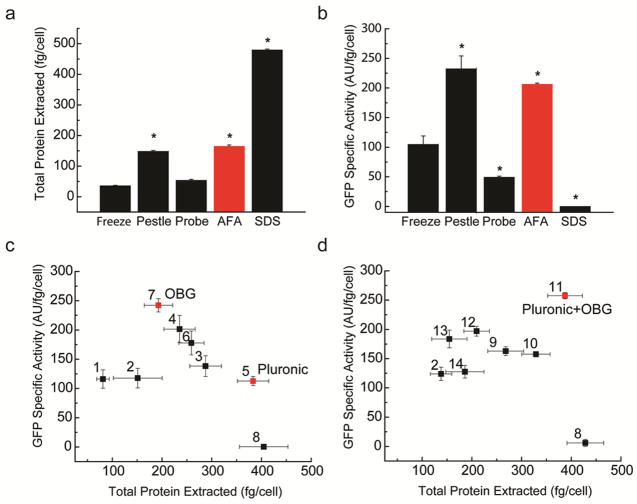
Fig. 1.
Focused acoustic sonication and pestle homogenization preserve native protein activity during cellular disruption. Total protein extracted (a) and GFP fluorescence (b) from Jurkat-GFP cells disrupted using freeze-thaw (Freeze), pestle homogenization (Pestle), probe sonication (Probe), focused acoustic sonication (AFA), or boiling in the presence of 1% sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS). Addition of poloxamer (Pluronic F-127) and octyl-β-glucoside (OBG) is superior to conventionally used detergents and maximizes native protein. GFP fluorescence of lysates as a function of total protein extracted for Jurkat-GFP cells disrupted using focused acoustic sonication in 150 mM NaCl, 50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, and supplemented with 1% individual detergents (c), or binary mixtures of 1% detergents (d), as labeled. Complete lists of detergents are listed in Supp. Table 1. Lysis in 1% SDS (SDS) serves as the positive control for total available cellular protein, and freeze-thaw in the absence of detergents (Freeze) is the control for unperturbed GFP fluorescence activity. Error bars represent standard deviations of three biologic replicates. * p < 0.01 for two-tailed t-test as compared to AFA and SDS.