Abstract
Three proteins, GTPase activating protein (GAP), neurofibromatosis 1 (NF1) and the yeast inhibitory regulator of the RAS-cAMP pathway (IRA2), have the ability to stimulate the GTPase activity of Ras proteins from higher animals or yeast. Previous studies indicate that certain lipids are able to inhibit this activity associated with the mammalian GAP protein. Inhibition of GAP would be expected to biologically activate Ras protein. In these studies arachidonic acid is shown also to inhibit the activity of the catalytic fragments of the other two proteins, mammalian NF1 and the yeast IRA2 proteins. In addition, phosphatidic acid (containing arachidonic and stearic acid) was inhibitory for the catalytic fragment of NF1 protein, but did not inhibit the catalytic fragments of GAP or IRA2 proteins. These observations emphasize the biochemical similarity of these proteins and provide support for the suggestion that lipids might play an important role in their biological control, and therefore also in the control of Ras activity and cellular proliferation.
Full text
PDF
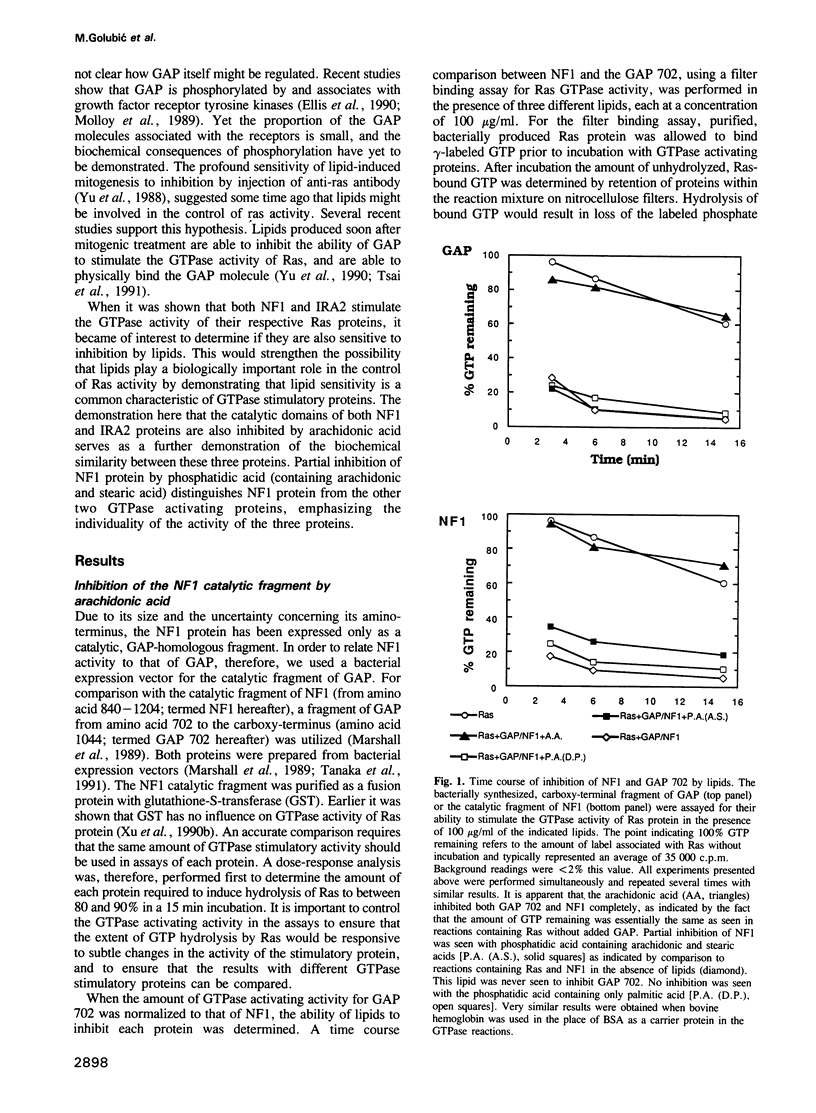





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ballester R., Marchuk D., Boguski M., Saulino A., Letcher R., Wigler M., Collins F. The NF1 locus encodes a protein functionally related to mammalian GAP and yeast IRA proteins. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):851–859. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90151-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bos J. L. ras oncogenes in human cancer: a review. Cancer Res. 1989 Sep 1;49(17):4682–4689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cawthon R. M., Weiss R., Xu G. F., Viskochil D., Culver M., Stevens J., Robertson M., Dunn D., Gesteland R., O'Connell P. A major segment of the neurofibromatosis type 1 gene: cDNA sequence, genomic structure, and point mutations. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):193–201. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90253-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis C., Moran M., McCormick F., Pawson T. Phosphorylation of GAP and GAP-associated proteins by transforming and mitogenic tyrosine kinases. Nature. 1990 Jan 25;343(6256):377–381. doi: 10.1038/343377a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farnsworth C. L., Marshall M. S., Gibbs J. B., Stacey D. W., Feig L. A. Preferential inhibition of the oncogenic form of RasH by mutations in the GAP binding/"effector" domain. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):625–633. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90246-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall A. ras and GAP--who's controlling whom? Cell. 1990 Jun 15;61(6):921–923. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90054-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan D. R., Morrison D. K., Wong G., McCormick F., Williams L. T. PDGF beta-receptor stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of GAP and association of GAP with a signaling complex. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):125–133. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90220-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazlauskas A., Ellis C., Pawson T., Cooper J. A. Binding of GAP to activated PDGF receptors. Science. 1990 Mar 30;247(4950):1578–1581. doi: 10.1126/science.2157284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall M. S., Hill W. S., Ng A. S., Vogel U. S., Schaber M. D., Scolnick E. M., Dixon R. A., Sigal I. S., Gibbs J. B. A C-terminal domain of GAP is sufficient to stimulate ras p21 GTPase activity. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1105–1110. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03480.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin G. A., Viskochil D., Bollag G., McCabe P. C., Crosier W. J., Haubruck H., Conroy L., Clark R., O'Connell P., Cawthon R. M. The GAP-related domain of the neurofibromatosis type 1 gene product interacts with ras p21. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):843–849. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90150-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molloy C. J., Bottaro D. P., Fleming T. P., Marshall M. S., Gibbs J. B., Aaronson S. A. PDGF induction of tyrosine phosphorylation of GTPase activating protein. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):711–714. doi: 10.1038/342711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulcahy L. S., Smith M. R., Stacey D. W. Requirement for ras proto-oncogene function during serum-stimulated growth of NIH 3T3 cells. Nature. 1985 Jan 17;313(5999):241–243. doi: 10.1038/313241a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawson T. Non-catalytic domains of cytoplasmic protein-tyrosine kinases: regulatory elements in signal transduction. Oncogene. 1988 Nov;3(5):491–495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers S., Kataoka T., Fasano O., Goldfarb M., Strathern J., Broach J., Wigler M. Genes in S. cerevisiae encoding proteins with domains homologous to the mammalian ras proteins. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):607–612. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90340-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serth J., Lautwein A., Frech M., Wittinghofer A., Pingoud A. The inhibition of the GTPase activating protein-Ha-ras interaction by acidic lipids is due to physical association of the C-terminal domain of the GTPase activating protein with micellar structures. EMBO J. 1991 Jun;10(6):1325–1330. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07651.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stacey D. W., Tsai M. H., Yu C. L., Smith J. K. Critical role of cellular ras proteins in proliferative signal transduction. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1988;53(Pt 2):871–881. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1988.053.01.100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Lin B. K., Wood D. R., Tamanoi F. IRA2, an upstream negative regulator of RAS in yeast, is a RAS GTPase-activating protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):468–472. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Nakafuku M., Satoh T., Marshall M. S., Gibbs J. B., Matsumoto K., Kaziro Y., Toh-e A. S. cerevisiae genes IRA1 and IRA2 encode proteins that may be functionally equivalent to mammalian ras GTPase activating protein. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):803–807. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90094-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trahey M., McCormick F. A cytoplasmic protein stimulates normal N-ras p21 GTPase, but does not affect oncogenic mutants. Science. 1987 Oct 23;238(4826):542–545. doi: 10.1126/science.2821624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai M. H., Hall A., Stacey D. W. Inhibition by phospholipids of the interaction between R-ras, rho, and their GTPase-activating proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):5260–5264. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.5260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai M. H., Roudebush M., Dobrowolski S., Yu C. L., Gibbs J. B., Stacey D. W. Ras GTPase-activating protein physically associates with mitogenically active phospholipids. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2785–2793. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai M. H., Yu C. L., Wei F. S., Stacey D. W. The effect of GTPase activating protein upon ras is inhibited by mitogenically responsive lipids. Science. 1989 Jan 27;243(4890):522–526. doi: 10.1126/science.2536192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viskochil D., Buchberg A. M., Xu G., Cawthon R. M., Stevens J., Wolff R. K., Culver M., Carey J. C., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A. Deletions and a translocation interrupt a cloned gene at the neurofibromatosis type 1 locus. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):187–192. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90252-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace M. R., Marchuk D. A., Andersen L. B., Letcher R., Odeh H. M., Saulino A. M., Fountain J. W., Brereton A., Nicholson J., Mitchell A. L. Type 1 neurofibromatosis gene: identification of a large transcript disrupted in three NF1 patients. Science. 1990 Jul 13;249(4965):181–186. doi: 10.1126/science.2134734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu G. F., Lin B., Tanaka K., Dunn D., Wood D., Gesteland R., White R., Weiss R., Tamanoi F. The catalytic domain of the neurofibromatosis type 1 gene product stimulates ras GTPase and complements ira mutants of S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):835–841. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90149-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu G. F., O'Connell P., Viskochil D., Cawthon R., Robertson M., Culver M., Dunn D., Stevens J., Gesteland R., White R. The neurofibromatosis type 1 gene encodes a protein related to GAP. Cell. 1990 Aug 10;62(3):599–608. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90024-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu C. L., Tsai M. H., Stacey D. W. Cellular ras activity and phospholipid metabolism. Cell. 1988 Jan 15;52(1):63–71. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90531-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu C. L., Tsai M. H., Stacey D. W. Serum stimulation of NIH 3T3 cells induces the production of lipids able to inhibit GTPase-activating protein activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6683–6689. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang K., DeClue J. E., Vass W. C., Papageorge A. G., McCormick F., Lowy D. R. Suppression of c-ras transformation by GTPase-activating protein. Nature. 1990 Aug 23;346(6286):754–756. doi: 10.1038/346754a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Corven E. J., Groenink A., Jalink K., Eichholtz T., Moolenaar W. H. Lysophosphatidate-induced cell proliferation: identification and dissection of signaling pathways mediated by G proteins. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):45–54. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90868-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]