Fig. 2.
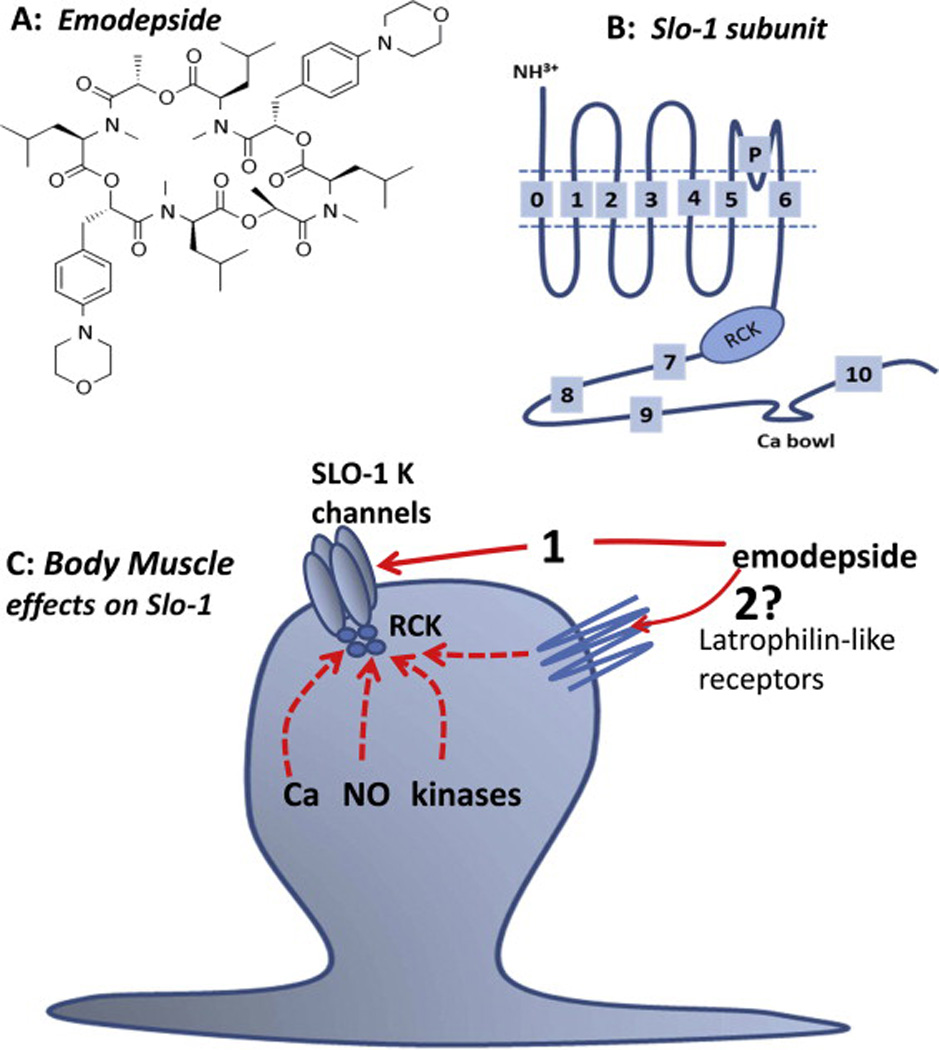
Summary diagrams of emodepside structure, Slo-1 subunit and a model of the mode action of emodepside on nematode body muscle. A: Emodepside. B: Line diagram of structure of one SLO-1 subunit; each SLO-1 K+ channel is made up of 4 of these subunits. C. Putative mode of action of emodepside on SLO-1 K+ channels in the muscle: act directly (1) or indirectly by stimulating latrophilin-like receptors (2) and signaling cascades that may involve NO, protein Kinase C and/or calcium. It is unlikely that emodepside acts at the extracellular surface of the SLO-1 K+ channel because of the slow time course of its action. It is very lipophilic and could act in the lipid membrane phase on the SLO-1 K+ channel or move into the cytoplasm and act intracellularly. A SLO-1 K+ channel (C) is shown composed of 4 subunits along with the ‘RCK’ cytoplasmic regulatory region of the channel. (Martin et al., 2012)
