Fig. 6.
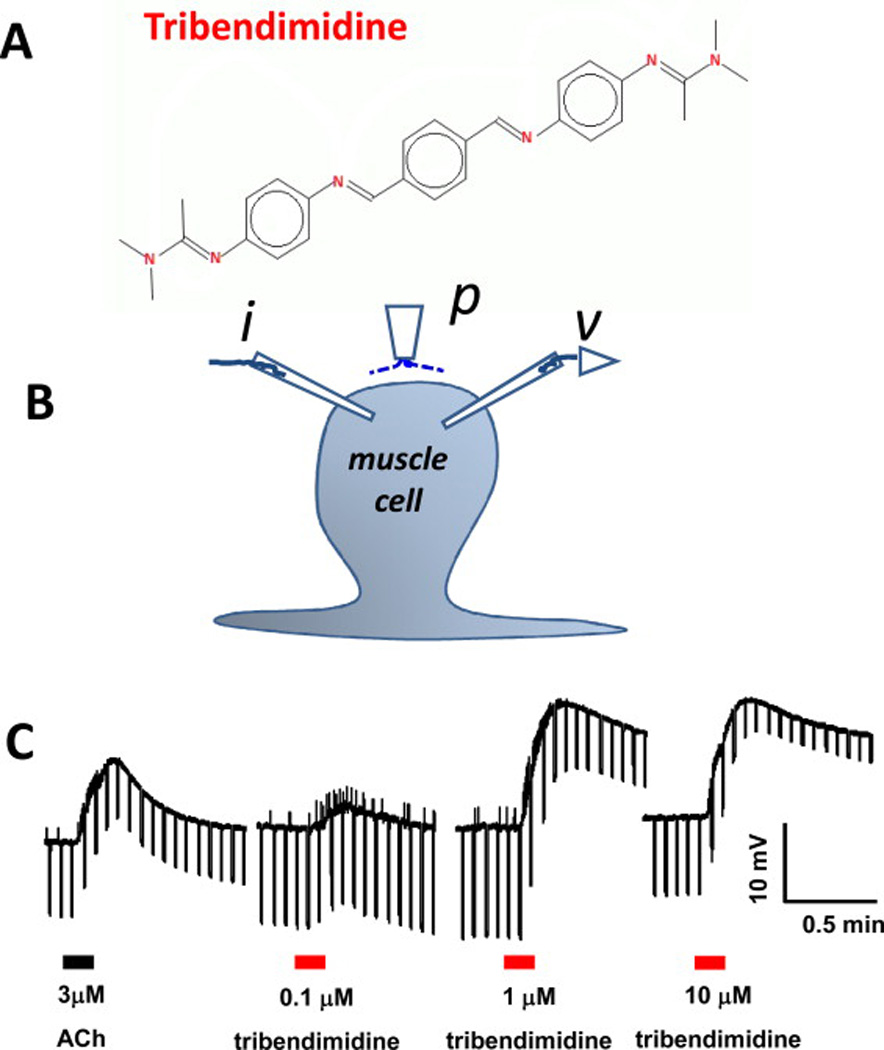
A: Chemical structure of tribendimidine. B: Diagram of the two-micropipette current-clamp technique used to record the membrane potential (v) and to inject 40 nA hyperpolarizing 500 ms current pulses (i) at 0.3 Hz. p is the microperfusion pipette used to apply and wash off the drugs. C: Application of 3 µM acetylcholine and then 0.1, 1 and 10 µM tribendimidine to the same preparation. 1 µM tribendimidine produces a bigger depolarization response (upward movement) and conductance increase (reduction in the voltage responses to current injection, producing a narrowing of the width of the trace) than 3 µM acetylcholine (Robertson et al., 2015).
