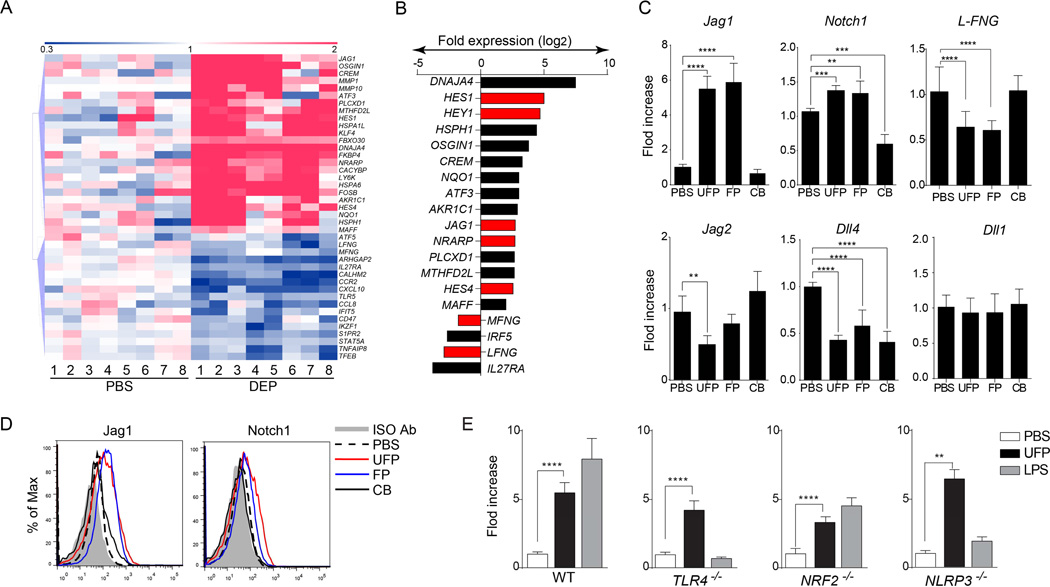
Fig 1.
PM induce components of the Notch pathway in human peripheral blood monocytes and mouse BMDCs. (A) Hierarchical clustering analysis of gene transcripts of human monocytes that were either sham treated with PBS or treated with DEP (10 µg/ml; 4h). (B) Gene expression fold change in human monocytes after treatment with DEP. Genes related to the Notch pathway are indicated in red. (C) mRNA expression of the indicated Notch pathway component in BMDCs treated with PBS, UFP, FP or CB (10 µg/ml each). (D) Flow cytometric analysis of Jag1 and Notch1 in murine BMDCs treated with PBS, FP, UFP or CB. (E) Fold change of Jag1 transcripts in BMDCs derived from either WT, Tlr4−/−, Nrf2−/− or Nlrp3−/− mice and treated with PBS, UFP (10 µg/ml) or LPS (1 µg/ml). For panels (A) and (B), results are representative of 1 experiment with N=8. For panels (C–E), results are representative of 3 independent experiments. N=10/15 mice per group. *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001. 1-way ANOVA with post-test analysis and Student’s unpaired two tailed t test.