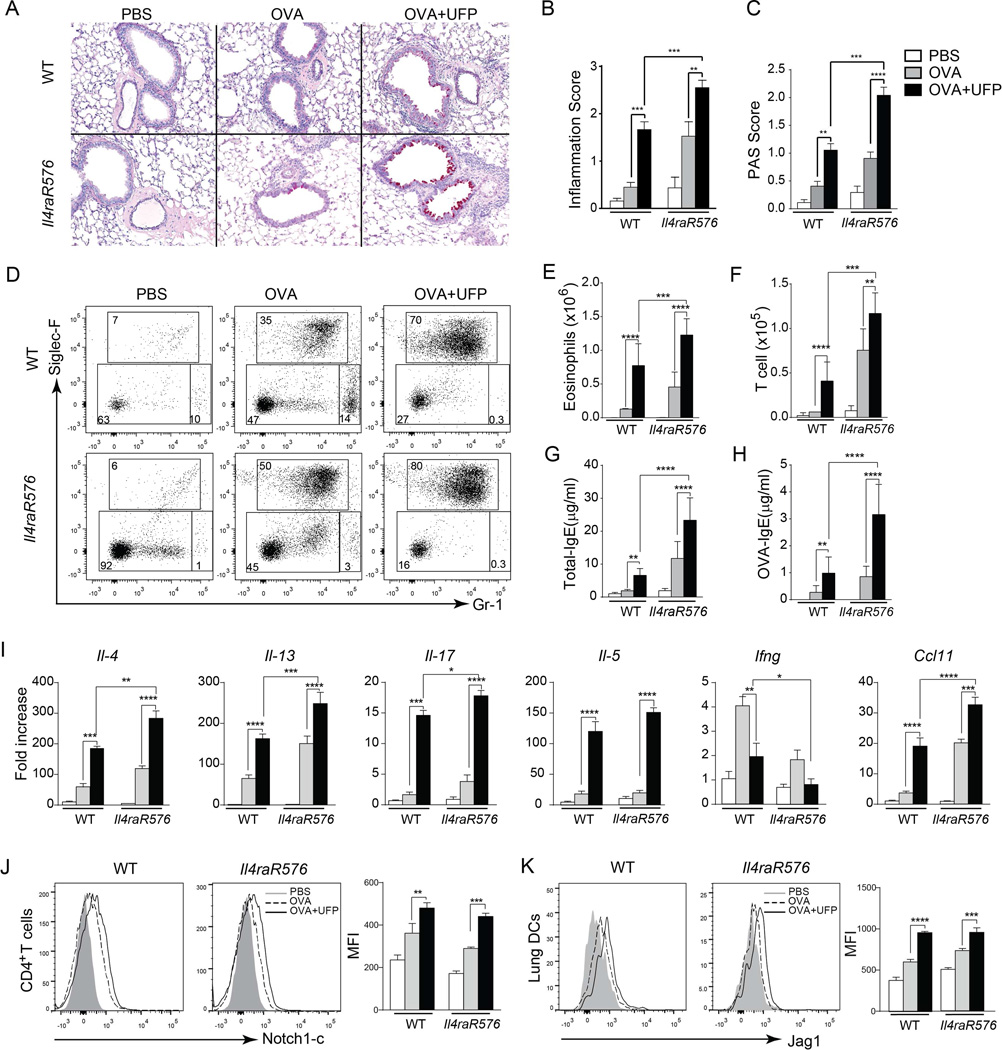
Fig 3.
UFP synergizes with Il4raR576 to promote OVA-induced allergic airway inflammation. (A) Representative PAS staining of lung sections isolated from WT and Il4raR576 mice immunized/challenged with PBS/OVA (PBS), OVA/OVA (OVA) or OVA/ OVA+UFP (OVA+UFP) (200× magnification). (B and C) Inflammation score (B) and PAS scores (C) from the mouse groups shown in (A). (D) Flow cytometric analysis of eosinophils (Siglec-F+Gr-1intermediate) and neutrophils (Siglec-F−Gr-1high) in the BAL fluid of them mouse groups described in panel (A). Numbers indicate the average frequencies of the respective population in each rectangle. (E and F). Eosinophils (E) and T cells (F) absolute numbers in the BAL fluid of the mouse groups described in panel (A). (G and H) Total (G) and OVA-specific (H) IgE levels in the serum of the mouse groups described in panel (A). (I) Il4, Il13, Il17, Il5, Ifng, Ccl11 mRNA expression in WT and Il4raR576 mice lung tissues after PBS, OVA or OVA-UFP treatment. (J and K) Flow cytometric analysis of Notch1-c (J) and Jag1 (K) expression by the CD4+ T cells isolated from the lungs of the mouse groups described in panel (A). Results are representative of 3 independent experiments. N=5 mice/group. *p<0.05, **<0.01, ***<0.001, ****<0.0001 by two way ANOVA with Bonferroni post test analysis.