Figure 5. Gi-Gq Balance Model of the Mechanism of Action of Antipsychotic and Psychedelic Drugs through the mGluR2/2AR Complex.
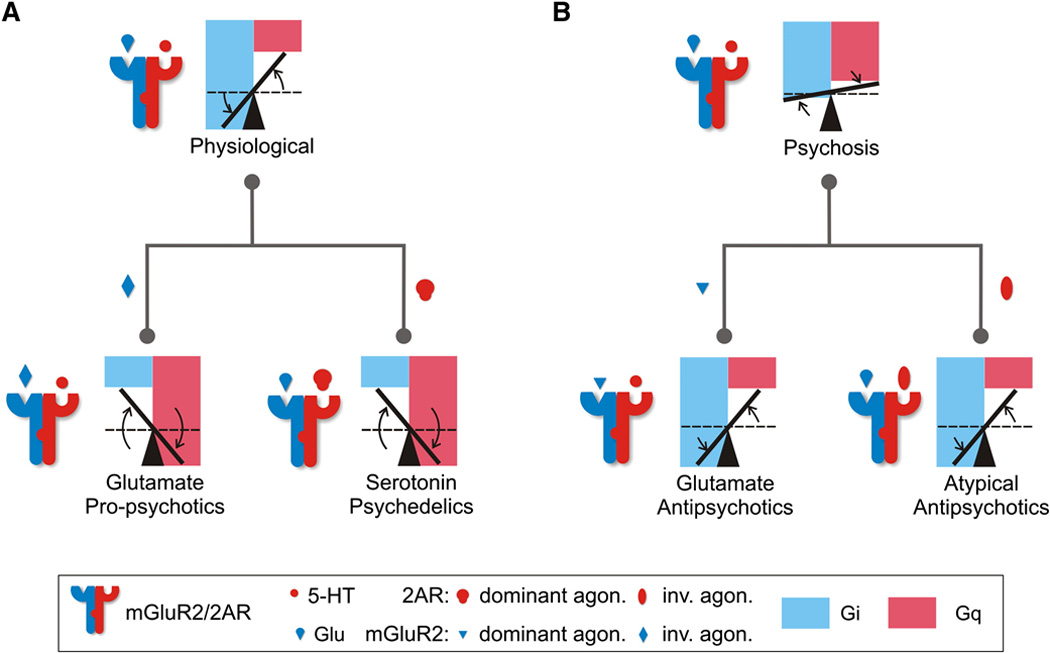
(A) Heteromerization of mGlu2R and 5-HT2AR establishes an optimal Gi-Gq signaling balance in response to the endogenous neurotransmitters, glutamate and serotonin (an increase in Gi and a decrease in Gq when compared to the homomeric receptor signaling; dashed lines). Psychedelics (mGlu2R inverse agonists and 5-HT2AR agonists) invert the signaling balance through the complex tipping the balance from being in favor of Gi signaling (normal complex) to becoming in favor of Gq signaling (propsychotic). (B) Disruption of the optimal balance in psychotic states can be compensated for by antipsychotics (mGlu2R agonists and 5-HT2AR inverse agonists) that tip the balance in favor of Gi signaling thus restoring the physiological signaling. Figure reprinted from Fribourg et al. [21].
