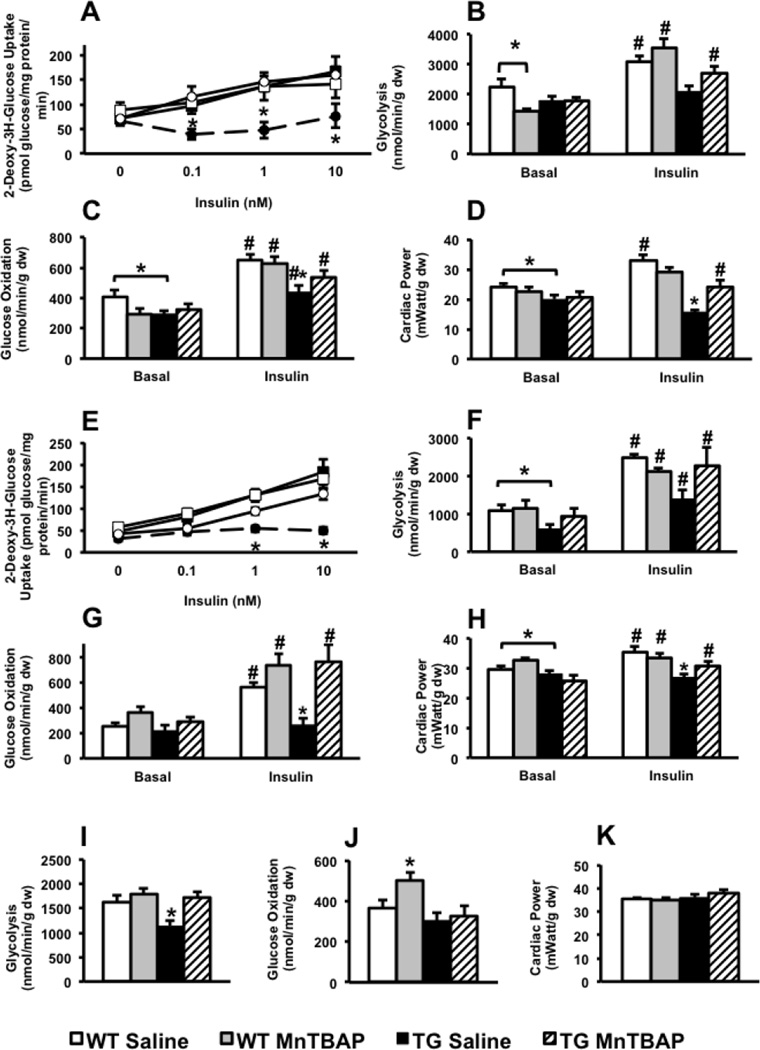
Figure 6. Impact of MnTBAP on insulin-stimulated cardiomyocyte glucose uptake and myocardial glucose utilization in 13 and 24-week-old UCP-DTA mice.
A. Insulin-stimulated 2-deoxy-3H-glucose uptake in isolated cardiomyocytes from 13 week-old and control hearts treated with saline or MnTBAP (n=4–5). B–D. Glycolysis, glucose oxidation, and cardiac power measured in isolated working heart preparations with or without 1nM insulin in 13 week-old UCP-DTA and control mice (n=5–7). E. Insulin-stimulated 2-deoxy-3H-glucose uptake in isolated cardiomyocytes from 24 week-old UCP-DTA and control hearts treated with saline or MnTBAP (n=5–7). F–H. Glycolysis, glucose oxidation, and cardiac power measured in isolated working heart preparations with or without 1nM insulin in 24 week-old UCP-DTA or control mice (n=5–7). I–K. Glycolysis, glucose oxidation, and cardiac power in db/db hearts measured in isolated working heart preparations without insulin (n=3–4). *p<0.05 vs. other genotypes in the same treatment group; # p<0.05 for insulin- stimulated vs. basal state for same genotype.
 Saline-treated control wildtype (WT) mice,
Saline-treated control wildtype (WT) mice,  MnTBAP-treated WT mice,
MnTBAP-treated WT mice,  UCP-DTA or db/db mice treated with saline,
UCP-DTA or db/db mice treated with saline,  UCP-DTA or db/db mice, treated with MnTBAP. Dw=dry weight.
UCP-DTA or db/db mice, treated with MnTBAP. Dw=dry weight.