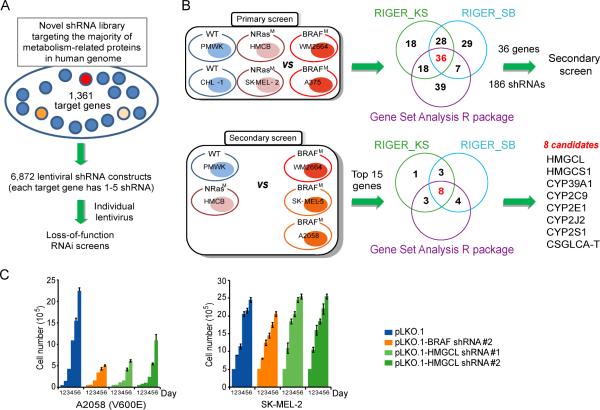
Figure 1. “Metabolism targeted” RNAi screens identify HMGCL as a synthetic lethal partner of BRAF V600E.
(A) Construction of a shRNA library systematically targeting human genes related to metabolism.
(B) Primary and secondary screening strategy. Supervised analysis of viability data (B-score) identified candidate genes that, when knocked down by shRNAs, distinguish BRAF V600E human melanoma cells (BRAFM) from mutant NRas cells (NRasM) and cells expressing wild-type BRAF and NRas (WT). Overlapped results of indicated statistical methods identified top 8 candidate genes.
(C) Effect of BRAF or HMGCL knockdown on melanoma cell proliferation rates assessed by daily cell counting. Data are mean±s.d.; n=3 each; p values were obtained by a two-tailed Student's t test.