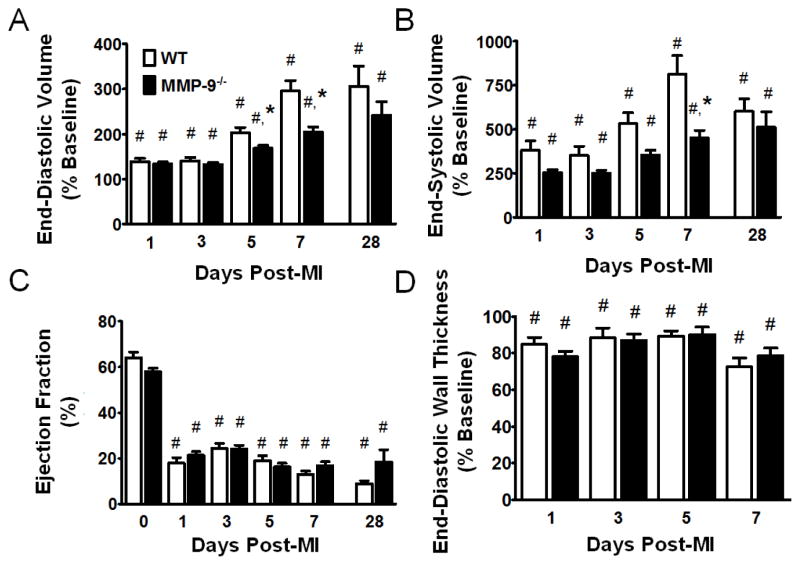
Figure 1. Matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) deletion reduces dilation of the left ventricle (LV) at days 5 and 7 post-myocardial infarction (MI).
A. MI resulted in increased end-diastolic volume in both groups at all time points (p<0.05). The change in end diastolic volume from baseline was significantly decreased in MMP-9−/− mice at day 5 and 7 post-MI. B. MI also resulted in increased end-systolic volume in both groups at all time points (p<0. 05). The change in end-systolic volume was significantly decreased in MMP-9−/− mice at day 7 post-MI. C. MI significantly reduced ejection fraction at all time points in both groups, and no significant differences were observed between the groups. D. MI led to a significant reduction in end-diastolic wall thickness in both groups, at each time-point (p<0.05), and no differences were observed between the WT and MMP-9−/− groups. Note that day 0–7 data is presented from serial images taken on the same mice, while day 28 data is from a different set of mice. (n=15–32 per group for day 0–7 groups and n=6 per group for day 28; #p<0.05 vs. corresponding baseline group, *p<0.05 vs. WT at corresponding day)