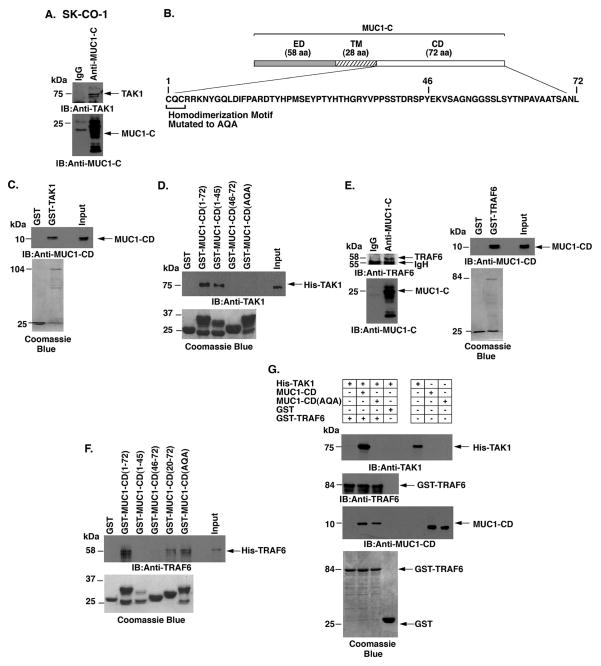
Figure 4. MUC1-C cytoplasmic domain binds directly to TAK1.
A. Lysates from SK-CO-1 cells were precipitated with anti-MUC1-C or a control IgG. The precipitates were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. B. Schematic representation of MUC1-C (ED, extracellular domain; TM, transmembrane domain) and the amino acid (aa) sequence of the cytoplasmic domain (CD). Highlighted is the CQC motif that is necessary for MUC1-C homodimerization and has been mutated to AQA in MUC1-CD. C. GST or GST-TAK1 was incubated with purified MUC1-CD. The adsorbates were immunoblotted with anti-MUC1-CD. Input of the GST proteins was assessed by Coomassie blue staining. D. GST, GST-MUC1-CD (full-length; 1-72) or the indicated GST-MUC1-CD mutants were incubated with His-TAK1. The adsorbates were immunoblotted with anti-TAK1. Input of the GST proteins was assessed by Coomassie blue staining. E. Lysates from SK-CO-1 cells were precipitated with anti-MUC1-C or a control IgG. The precipitates were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies (left). GST or GST-TRAF6 was incubated with purified MUC1-CD. The adsorbates were immunoblotted with anti-MUC1-CD (right). Input of the GST proteins was assessed by Coomassie blue staining (right). F. GST, GST-MUC1-CD(1-72) or the indicated GST-MUC1-CD mutants were incubated with His-TRAF6. The adsorbates were immunoblotted with anti-TRAF6. Input of the GST proteins was assessed by Coomassie blue staining. G. His-TAK1 was incubated with GST or GST-TRAF6 in the presence of MUC1-CD or MUC1-CD(AQA). Adsorbates and input proteins were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. Input of the GST-TRAF6 and GST proteins was assessed by Coomassie blue staining.