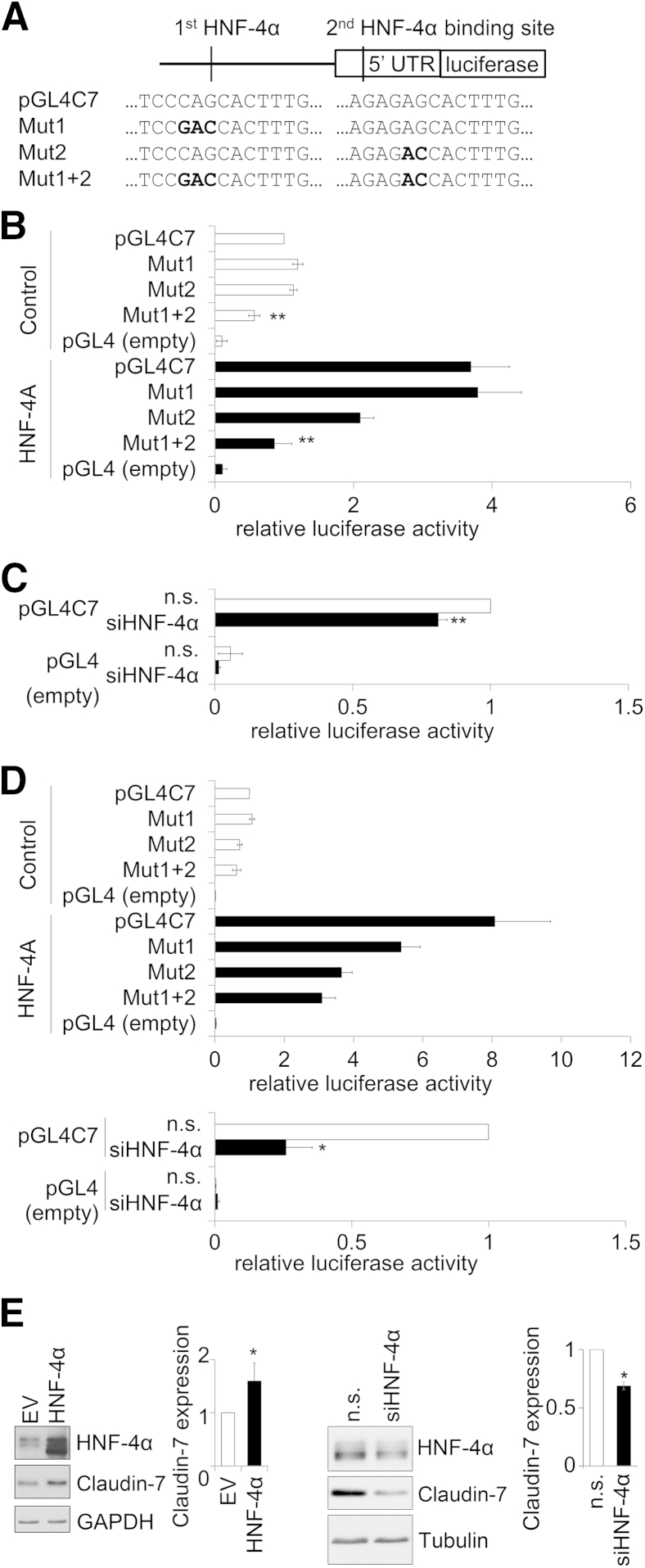
Figure 6.
CLDN7 regulation by HNF-4α, mutation analysis. A: HNF-4α binding motifs at −2524 bp (Mut1) or −861 bp (Mut2) from the start codon were mutated on the CLDN7 luciferase reporter. The mutations were introduced by PCR primers containing mismatches as indicated by bold letters. B: Luciferase assays were performed in Caco-2 model intestinal epithelial cells (IECs) to test the effect of mutated HNF-4α binding sequences on CLDN7 promoter activity (white bars). Mutation of one or the other HNF-4α binding sites does not change CLDN7 promoter activity. Simultaneous mutation of both HNF-4α binding motifs (Mut1+2) diminishes CLDN7 promoter activity. At the same time, HNF-4α is expressed exogenously in Caco-2 model IECs (black bars). Luciferase assay shows up-regulated CLDN7 promoter activity in response to increased HNF-4α expression compared with control vector–treated cells. This increase was reduced in the single mutant construct Mut2, whereas the double mutant abolished the exogenous HNF-4α–induced CLDN7 promoter activity. The data shown are average ± SEM of six independent experiments. C: Small interfering RNA (siRNA) knockdown of HNF-4α in Caco-2 cells results in a 20%, statistically significant, decrease in CLDN7 promoter activity. Data shown are the average ± SEM of three independent experiments. D: Luciferase assays performed in HT29/B6 model IECs yielded results similar to those in Caco-2 cells. Data are presented as the average ± SEM of four experiments for overexpression and three experiments for knockdown of HNF-4α. E: Exogenous HNF-4α increases claudin-7 protein levels by twofold in nondifferentiated Caco-2 IECs compared to empty vector (EV) treated cells. Representative blots and densitometry analysis (means ± SEM) of five blots for overexpression and three blots for knockdown are shown. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01. GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; n.s., nonspecific control RNA; UTR, untranslated region.